Fig 4.
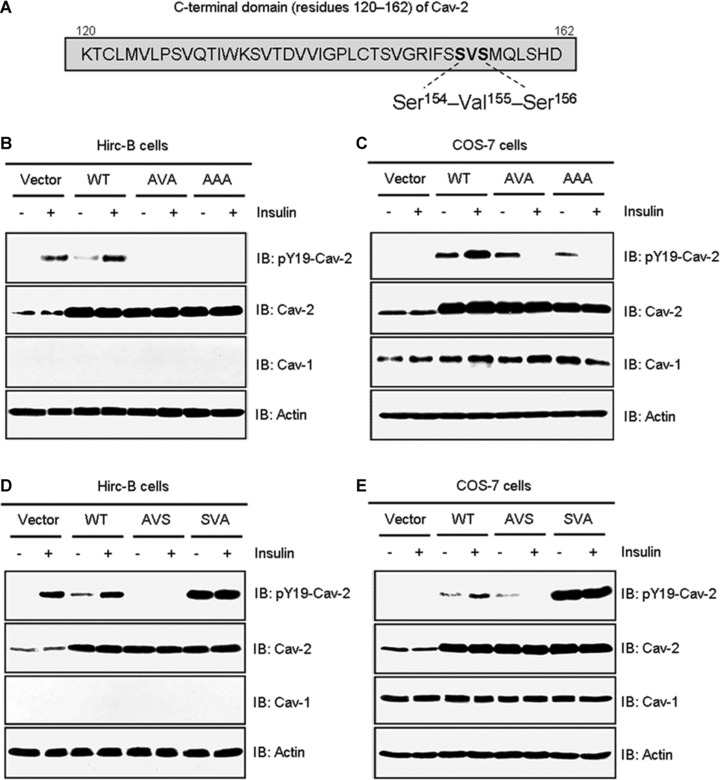
Effects of mutations in the Ser154–Val155–Ser156 domain on phosphorylation of pY19-cav-2 in response to insulin. (A) The Ser154–Val155–Ser156 domain in C-terminal residues 120–162 of cav-2. Hirc-B (B) and COS-7 (C) cells expressing pcDNA3 vector, WT-cav-2, AVA (S154A and S156A), or AAA (S154A, V155A and S156A) mutants were treated with or without insulin (100 nM) for 10 min. WCL were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies specific for pY19-cav-2, cav-2, cav-1 and actin. Shown is a representative experiment that was repeated three times. Hirc-B (D) and COS-7 (E) cells expressing pcDNA3 vector, WT-cav-2, AVS (S154A) or SVA (S156A) mutants were treated with or without insulin (100 nM) for 10 min. WCL were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies specific for pY19-cav-2, cav-2, cav-1 and actin as indicated. Shown is a representative experiment that was repeated three times.
