Fig 4.
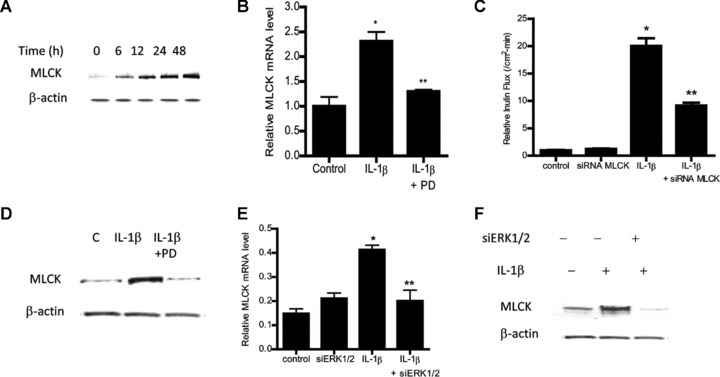
ERK1/2 inhibition prevented the IL-1β-induced up-regulation of Caco-2 MLCK. (A) Time-course effect of IL-1β on Caco-2 MLCK protein expression (β-actin was used as an internal control for protein loading). (B) IL-1β treatment caused an increase in Caco-2 MLCK mRNA. ERK1/2 inhibitor PD-98059 prevented the increase in MLCK mRNA levels. MLCK mRNA level was expressed relative to the control level which was assigned a value of 1. The average copy number of MLCK mRNA in controls was 4.63 × 1011 (means ± S.E., n= 5). *P < 0.001 versus control; **P < 0.001 versus IL-1β treatment. (C) MLCK siRNA transfection prevented the IL-1β-induced drop in Caco-2 TER. (D) MLCK siRNA-induced knockdown prevented the IL-1β-induced increase in inulin flux (means ± S.E., n= 5). *P < 0.001 versus control; **P < 0.001 versus IL-1β treatment. (E) ERK1/2 inhibitor PD-98059 prevented the IL-1β-induced up-regulation of MLCK protein expression. Effect of siRNA ERK1/2 transfection on IL-1β-induced increase in MLCK mRNA level (F) and increase in MLCK protein expression (G). siRNA-induced knockdown of ERK1/2 prevented the IL-1β-induced increase in MLCK mRNA and MLCK protein levels (means ± S.E., n= 4). *P < 0.001 versus control; **P < 0.001 versus IL-1β treatment.
