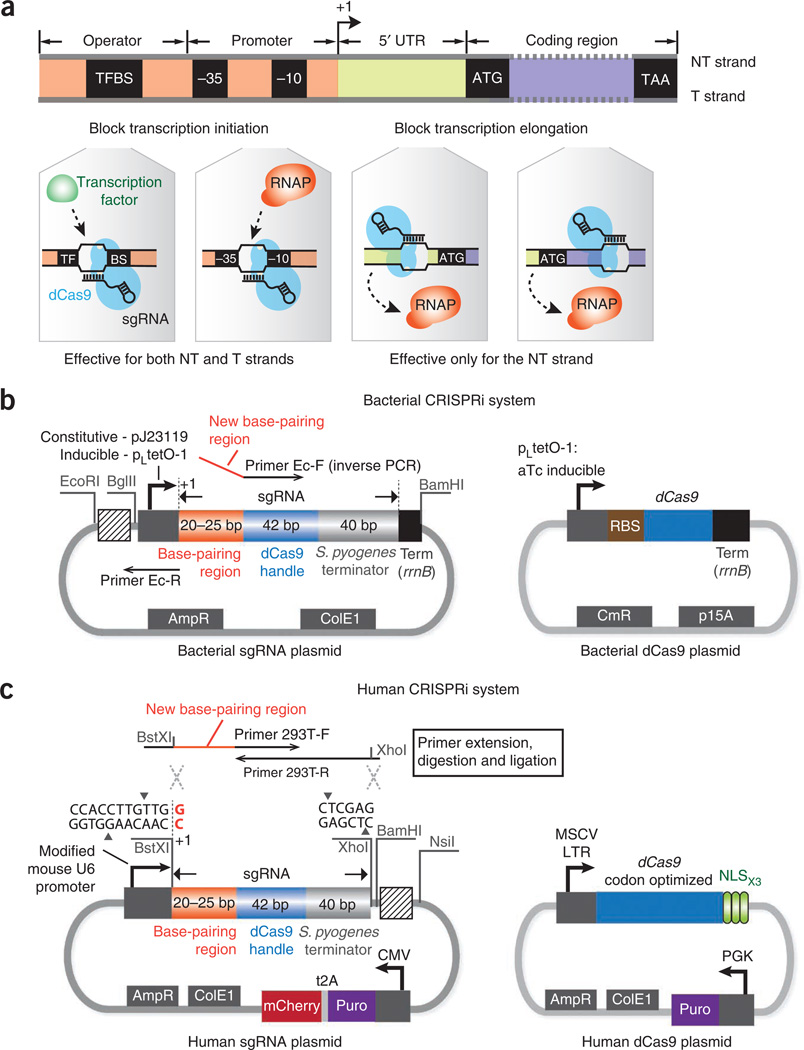
Figure 1.
The CRISPRi system for transcription repression in bacteria and human cells. (a) Depending on the target genomic locus, CRISPRi can block transcription elongation or initiation. When the dCas9-sgRNA complex binds to the nontemplate (NT) DNA strand of the UTR or the protein coding region, it can silence gene expression by blocking the elongating RNAPs. When the dCas9-sgRNA complex binds to the promoter sequence (e.g., the −35 or −10 boxes of the bacterial promoter) or the cis-acting transcription factor binding site (TFBS), it can block transcription initiation by sterically inhibiting the binding of RNAP or transcription factors to the same locus. Silencing of transcription initiation is independent of the targeted DNA strand. (b) The plasmid maps of the sgRNA and dCas9 expression vectors in E. coli. The sgRNA expression plasmid contains a promoter (constitutive—pJ23119 or inducible—pLtetO-1) with an annotated transcription start site (+1), an ampicillin-selectable marker (AmpR) and a ColE1 replication origin. The primer-binding sites for inverse PCR are highlighted. Three restriction sites EcoRI, BglII and BamHI are inserted to flank the sgRNA expression cassette to facilitate BioBrick cloning, so that new sgRNA cassettes can be repeatedly inserted into the striped box region. To ensure efficient transcription termination in E. coli, a strong terminator, rrnB, is added to the 3′ end of the sgRNA expression cassette. The dCas9 plasmid contains an aTc-inducible pLtetO-1 promoter, a strong ribosomal binding site (RBS), a chloramphenicol-resistance marker (CmR) and a p15A replication origin. (c) The plasmid maps used for sgRNA and dCas9 expression in human cells. The sgRNA expression plasmid is based on the pSico lentiviral vector that contains a mouse U6 promoter, an expression cassette consisting of a CMV promoter, a puromycin-resistance gene (Puro) and an mCherry gene for selection or screening of the plasmid, an ampicillin-selectable marker and a ColE1 replication origin for cloning in E. coli cells. Transcription of the U6 promoter starts at the last nucleotide G (red color) within the BstXI restriction site. New sgRNAs can be inserted between the BstXI and XhoI sites. The primer extension and insertion sites for sgRNA cloning are shown. The restriction sites BamHI and NsiI can be used to facilitate the BioBrick cloning: new sgRNA cassettes can be repeatedly inserted into the striped box region using BioBrick. The dCas9 plasmid contains a human codon-optimized dCas9 gene expressed from the murine stem cell virus (MSCV) long terminal repeat (LTR) promoter and is fused to three copies of the SV-40 NLS at the C terminus with a 3-aa linker. The plasmid also contains a puromycin-resistance gene controlled by the PGK promoter.