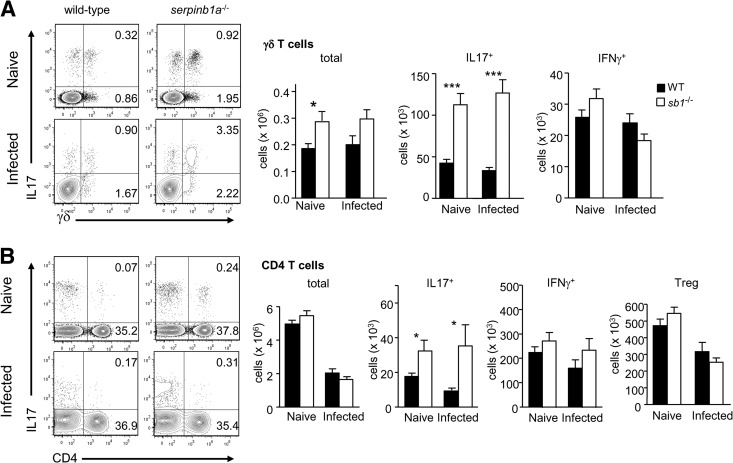
Figure 1. Increase of IL-17+ γδ and CD4 T cells in lungs of naive serpinb1a−/− mice.
Matched groups of WT and serpinb1a−/− mice were killed without infection or as a control on Day 2 of sublethal infection with influenza virus. Suspensions of lung cells were cultured with PMA and ionomyin (and brefeldin A) and stained with surface antibodies and intracellularly for IL-17 and IFN-γ. Cells were gated on lymphocytes (low side-scatter, CD45+CD11bneg) and then on γδ TCR or CD4. (A) γδ T cells. Shown left to right are representative contour plots, followed by quantitation of total, IL-17+, and IFN-γ+ γδ T cells. (B) CD4 T cells. Shown are contour plots followed by quantitation of total, IL-17+, and IFN-γ+ CD4 cells and Tregs (CD4+FoxP3+). Numbers in quadrants indicate percentage in each. Means ± sem for eight to 12 mice/group from two to three experiments. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. sb1−/−, serpinb1a−/−. Counts of monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils in naive lungs are shown in Supplemental Fig. 1.