Figure 1. Phage display affinity maturation to form a high affinity monoclonal antibody specific for apoA1 oxidized by the MPO-H2O2-halide system.
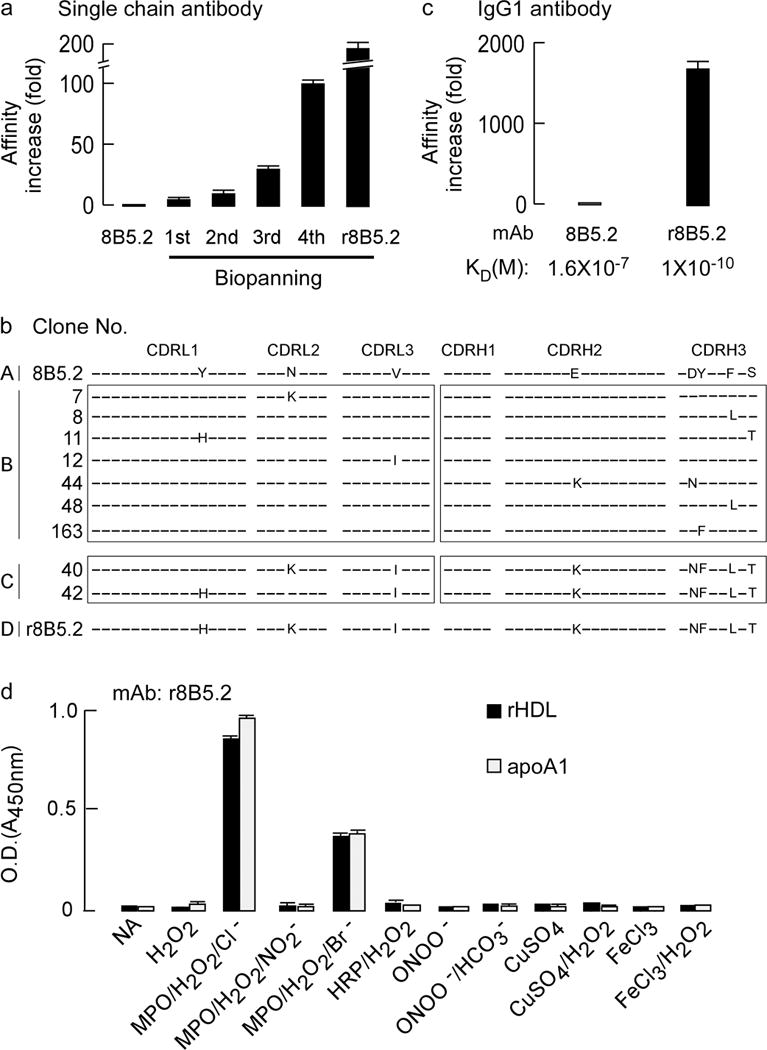
(a) Fold-increase in apparent binding affinity following multiple rounds of biopanning after phage display affinity maturation of parental mouse mAb 8B5.2 single chain antibody (scFv). (b) Complementarity determining region (CDR) DNA sequences of original mAb 8B5.2 and that of nine affinity matured scFv r8B5.2 subclones identified with lowest dissociation rate. CDRL1–3: CDRs of antibody light chain. CDRH1–3: CDRs of antibody heavy chain. The letters indicate identities of the mutated amino acids and differences between wild type and affinity matured clones. (c) The increase in apparent affinity (KD) of parental mAb 8B5.2 and affinity matured scFv r8B5.2 after conversion to full length mouse and human chimeric IgG1, designated as r8B5.2. (d) mAb r8B5.2 recognizes with high specificity only apoA1 or rHDL exposed to the MPO-H2O2-halide system, but not the indicated alternative oxidation systems. ApoA1 or rHDL were coated onto 96 well plates and detected with r8B5.2, as described in Methods. Data are mean± S.D. of triplicate determinations.
