Figure 2. Epitope mapping of affinity matured mAb r8B5.2.
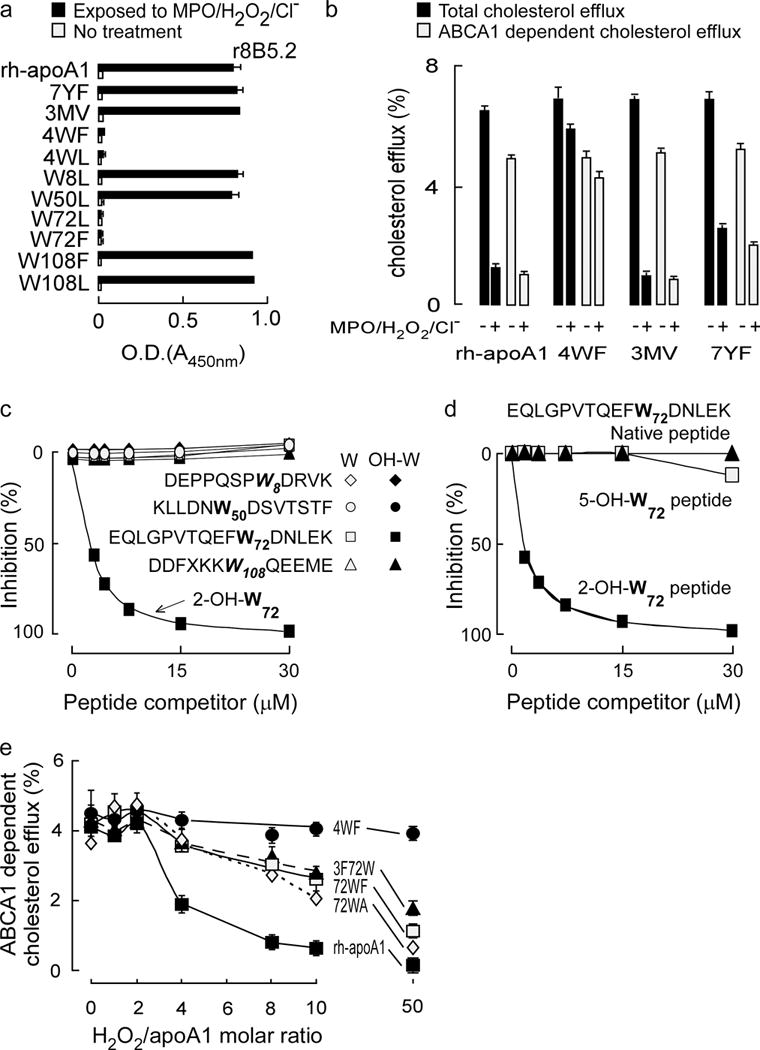
(a) Antibody (r8B5.2) reactivity against the indicated recombinant human apoA1 (rh-apoA1) and mutant forms was quantified before and following exposure to the MPO-H2O2-halide system. The ELISA studies were performed as described in Methods and identify oxidized Trp72 as a recognition epitope. (b) Total and ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux activities in RAW macrophages were performed with rh-apoA1 and the indicated mutant apoA1 forms before vs. following exposure to the MPO-H2O2-halide system, as described under Methods. (c,d): Competition ELISAs. Purified human apoA1 oxidized by the MPO/H2O2/Cl− system served as coating antigen. Antibody r8B5.2 binding was competed for with increasing concentrations of the various Trp-containing apoA1 competitor peptides incorporating either native (non-oxidized) Trp or 2-OH-Trp at the indicated positions in c. In d, either the peptide harboring native Trp, 2-OH-Trp or 5-OH-Trp corresponding to position 72 in the indicated apoA1 peptide sequence was used as the competitor. (e) Effect of Trp substitutions on rh-apoA1 ABCA1-dependent cellular cholesterol efflux function. The indicated rh-ApoA1 and mutant apoA1 proteins were exposed to the MPO/H2O2/Cl− oxidation system at the specified molar ratios of H2O2/apoA1 (0 to 10:1, mol:mol). Proteins were assayed for ABCA1-dependent cellular cholesterol acceptor activity as described in Methods. All data shown are means ± S.D. of at least triplicate determinations.
