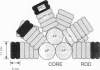
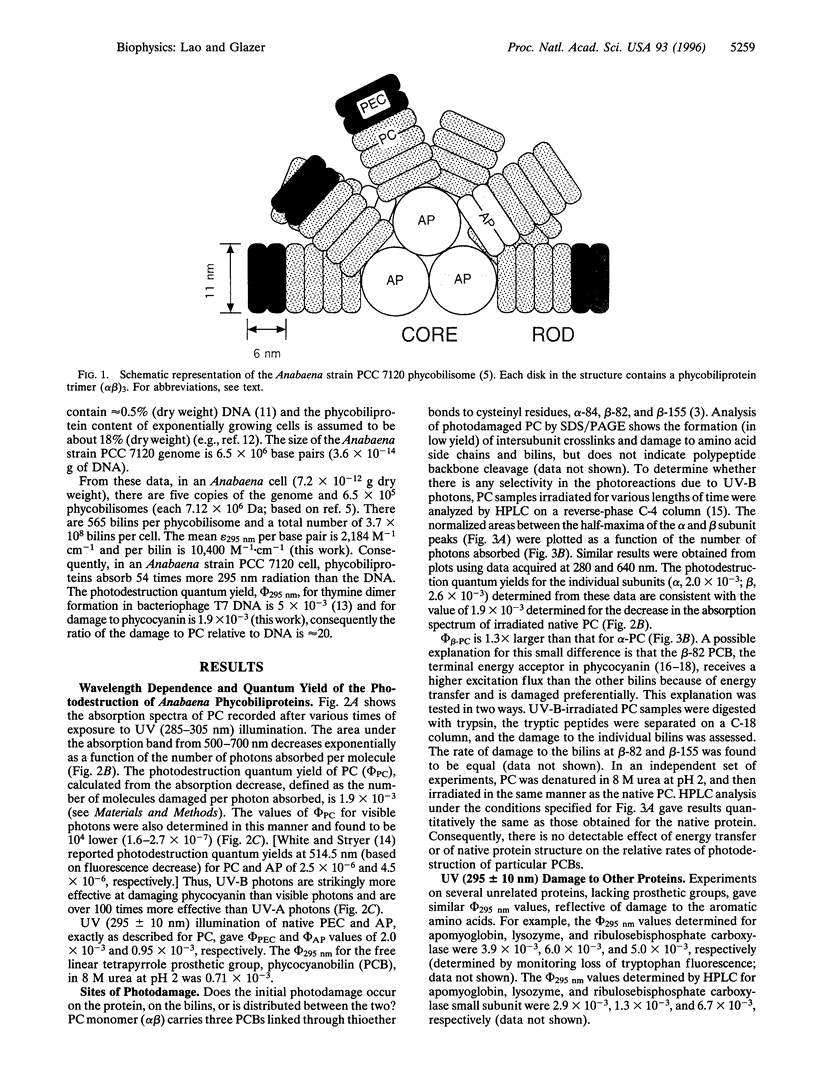
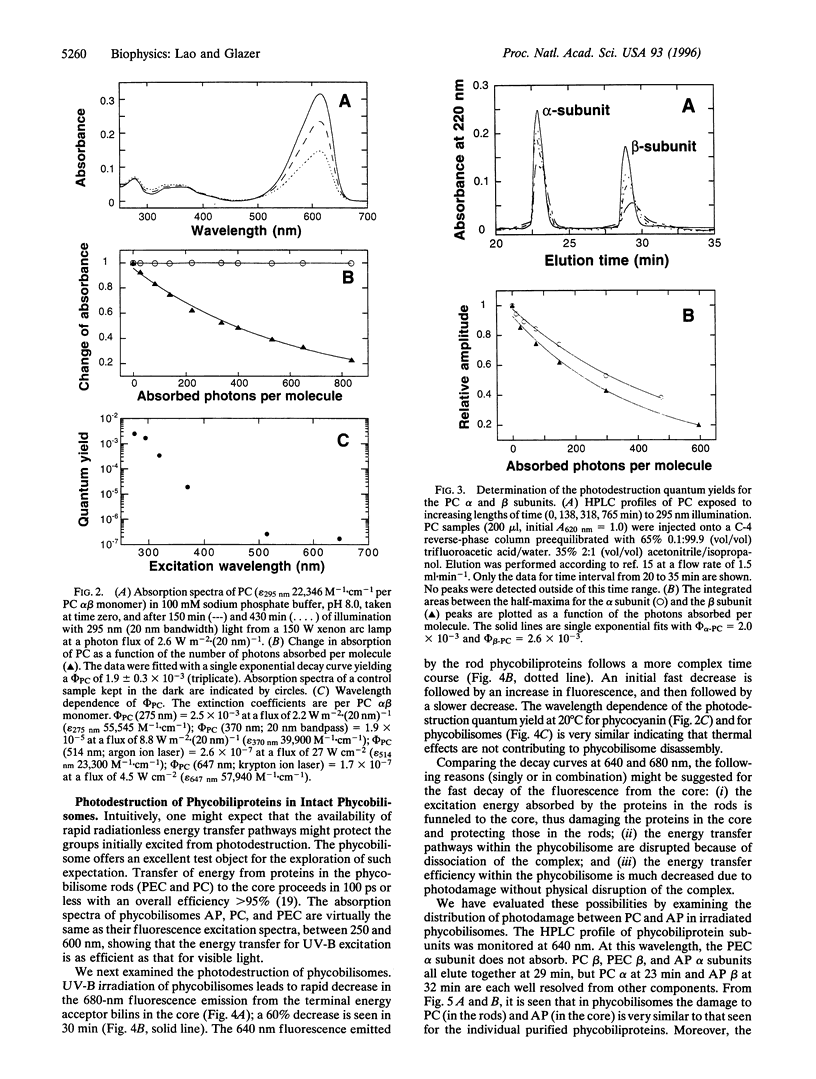
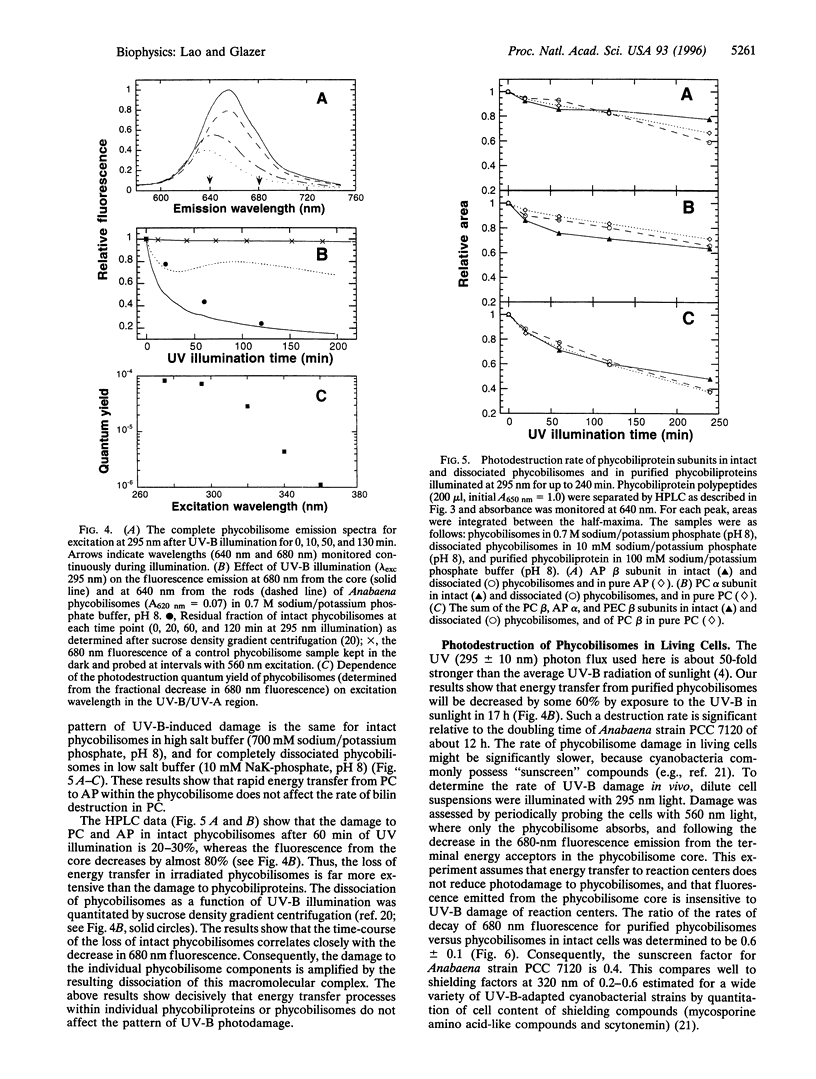
Abstract
Cyanobacteria are important contributors to global photosynthesis in both marine and terrestrial environments. Quantitative data are presented on UV-B-induced damage to the major cyanobacterial photosynthetic light harvesting complex, the phycobilisome, and to each of its constituent phycobiliproteins. The photodestruction quantum yield, phi295 nm, for the phycobiliproteins is high (approximately 10(-3), as compared with approximately 10(-7) for visible light). Energy transfer on a picosecond time scale does not compete with photodestruction. Photodamage to phycobilisomes in vitro and in living cells is amplified by causing dissociation and loss of function of the complex. In photosynthetic organisms, UV-B damage to light-harvesting complexes may significantly exceed that to DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. B., Arnon D. I. Studies on Nitrogen-Fixing Blue-Green Algae. I. Growth and Nitrogen Fixation by Anabaena Cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):366–372. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Bogorad L. Complementary chromatic adaptation in a filamentous blue-green alga. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):419–435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. A., Glazer A. N., Eiserling F. A. Characterization and structural properties of the major biliproteins of Anabaena sp. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Oct 11;110(1):61–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00416970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig I. W., Leach C. K., Carr N. G. Studies with deoxyribonucleic acid from blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;65(3):218–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00407105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pichel F., Castenholz R. W. Occurrence of UV-Absorbing, Mycosporine-Like Compounds among Cyanobacterial Isolates and an Estimate of Their Screening Capacity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):163–169. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.163-169.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauser M., Bryant D. A., Frank G., Wehrli E., Rusconi S. S., Sidler W., Zuber H. Phycobilisome structure in the cyanobacteria Mastigocladus laminosus and Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Eur J Biochem. 1992 May 1;205(3):907–915. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N. Light guides. Directional energy transfer in a photosynthetic antenna. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N. Phycobiliproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1988;167:291–303. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)67034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N., Yeh S. W., Webb S. P., Clark J. H. Disk-to-Disk Transfer as the Rate-Limiting Step for Energy Flow in Phycobilisomes. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):419–423. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4685.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N. T., Thiel T., Giddings T. H., Jr, Wolk C. P. New Anabaena and Nostoc cyanophages from sewage settling ponds. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):236–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong L. J., Glazer A. N. Phycoerythrins of marine unicellular cyanobacteria. I. Bilin types and locations and energy transfer pathways in Synechococcus spp. phycoerythrins. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9515–9527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolarski R., Bojkov R., Bishop L., Zerefos C., Staehelin J., Zawodny J. Measured trends in stratospheric ozone. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):342–349. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. V., Glazer A. N. Phycobiliprotein methylation. Effect of the gamma-N-methylasparagine residue on energy transfer in phycocyanin and the phycobilisome. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90293-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. V., Glazer A. N. Separation of phycobiliprotein subunits by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1990 Aug 1;188(2):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90609-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Schoenlein R. W., Peteanu L. A., Mathies R. A., Shank C. V. Vibrationally coherent photochemistry in the femtosecond primary event of vision. Science. 1994 Oct 21;266(5184):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.7939680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. C., Stryer L. Photostability studies of phycobiliprotein fluorescent labels. Anal Biochem. 1987 Mar;161(2):442–452. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90473-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh S. W., Ong L. J., Glazer A. N. Role of phycoerythrin in marine picoplankton Synechococcus spp. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1422–1424. doi: 10.1126/science.3097824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]