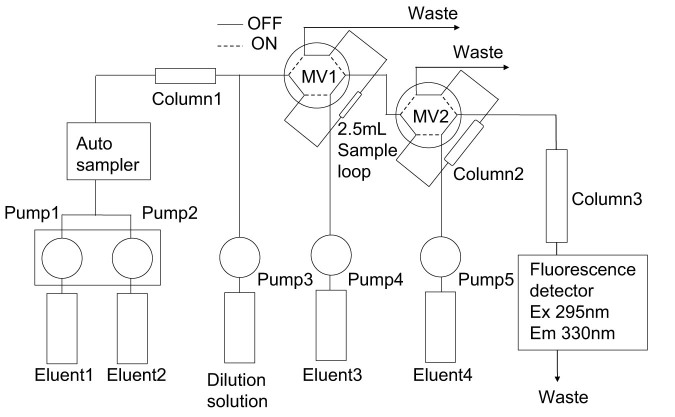
Figure 1. Schematic diagram.
An anion-exchange chromatography is composed of a column (Column1), two pump (Pump1 and 2), two eluents (Eluent1 and 2), and an auto sampler. The flow rate of the mixed eluent is 0.25 mL/min. The eluents (Eluent1 and 2) contained 0 and 500 mmol/L sodium perchlorate, respectively. The concentrations of sodium perchlorate for elution of HDL, LDL, and VLDL from the column (Column1) are 95, 130, and 165 mmol/L, respectively. The HDL, LDL, and VLDL fractions were mixed with a dilution solution (70% ethanol + 1% TritonX-100). The flow rate of Pump3 is 0.25 mL/min. The samples mixed with the dilution solution are injected into Column2 by changing MV1 from OFF-position to ON-position. A reversed-phase chromatography is composed of two column (Column2 and 3) which packed with octadecyl-ligand porous silica-based gel, 2 pumps (Pump4 and 5), two eluents (Eluent3 and 4), two mortar valves (MV1 and 2), and fluorescent detector. The eluents (Eluent1 and 2) contain 30.0 and 83.5% ethanol, respectively. Each flow rate of Pump4 and 5 is 1.5 mL/min.