Figure 5.
Ectopic Expression of PRDM1 in hESCs Enhances Embryonic Germ Cell Differentiation
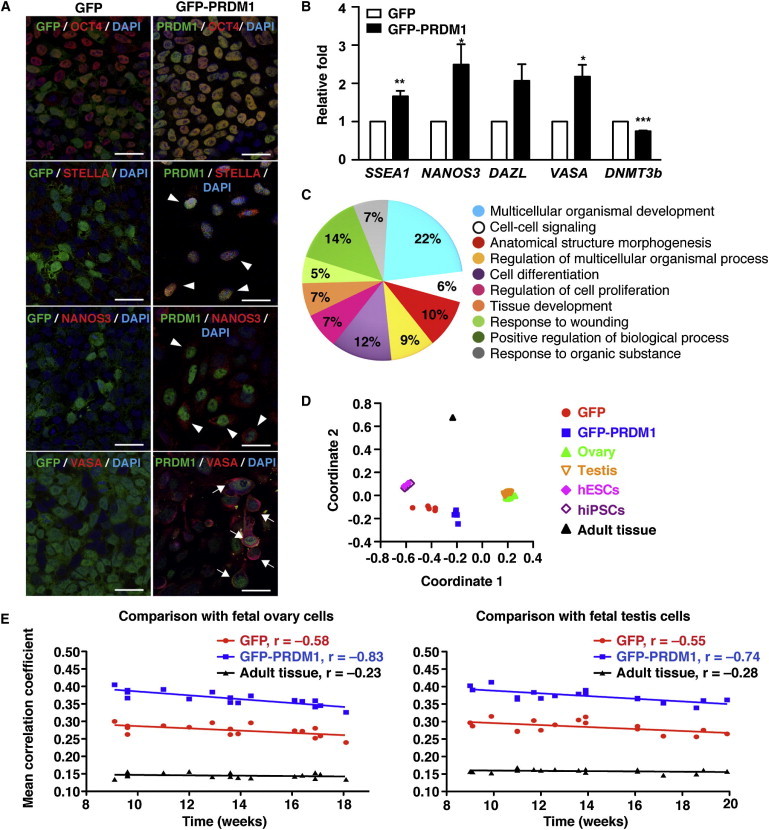
(A) Immunofluorescence staining shows that ectopic expression of PRDM1 coexpressed with OCT4+ cells, and produced STELLA+ and NANOS3+ (indicated by the arrowheads), and VASA+ (indicated by the arrows) cells in H9 hESCs. GFP-PRDM1- or GFP-expressing H9 colonies were picked under the fluorescence microscope 7 days after lentiviral transduction and the GFP+ cells were seeded onto a new feeder layer, followed by the immunofluorescence staining and DAPI staining at week 2. Scale bar, 30 μm.
(B) qRT-PCR for the indicated mRNA using cDNA from isolated GFP+ H9 cells that expressed either GFP-PRDM1 or GFP for 2 weeks as described in (A). Results are the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.
(C) GO analysis showed a significant enrichment of genes related to differentiation and development following PRDM1 expression in H9 cells. The list shows the top ten enriched GO terms based on the p value. The percentage represents the relative numbers of genes belonging to each category within the top ten enriched GO terms of 1,071 preferentially expressed genes.
(D) Multidimensional scaling plot of the 51 global gene-expression profiles of selected stem cells and tissue samples. Distances between data points approximate dissimilarity (1 − correlation coefficient) of their expression profiles.
(E) The average correlation coefficients between the expression profiles of H9 hESCs transduced with GFP- or GFP-PRDM1-expressing vector and fetal ovary (left) or testis (right) tissues at the indicated developmental time points.
