Figure 7.
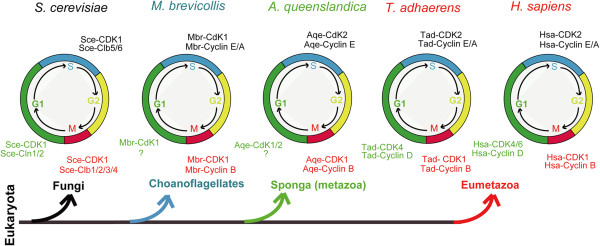
Schematic scenarios of CDK and cyclin protein function in cell cycle regulation of different representative organisms. Schemes for organisms S. cerevisiae and H. sapiens were drawn based on previous reports [6,37,67,70], and schemes for M. brevicollis, A. queenslandica, and T. adhaerens were drawn based on inferences derived from our evolutionary analysis (see text for further explanations). Accession numbers of CDK and cyclin proteins in the figure are as follows: Sce-CDK1: gi:6319636; Sce-Cln1/2: gi:6323855, gi:6324999; Sce-Clb5/6: gi:6325377, gi:6321546; Sce-Clb1/2/3/4: gi:6321545, gi:6325376, gi:6320046, gi:6323239; Mbr-CdK1: gi:167517533; Mbr-cyclin B: gi:167523717, gi:167524669; Mbr-cyclin E: gi:167519314; Mbr-cyclin A: gi:167517989; Aqe-CDK1: gi:340381019, Aqe-CdK2: gi:340379293; Aqe-cyclin B: gi:340376468, gi:340374274; Aqe-cyclin E: gi:340379787; Tad- CDK1: gi:196003954; Tad-CDK2: 196013348; Tad-CDK4: gi:195999760; Tad-cyclin B: gi:196002535; gi:196003740; Tad-cyclin E: gi:196003236; Tad-cyclin A: gi:196005765; Tad-cyclin D: gi:196001479.
