Figure 4.
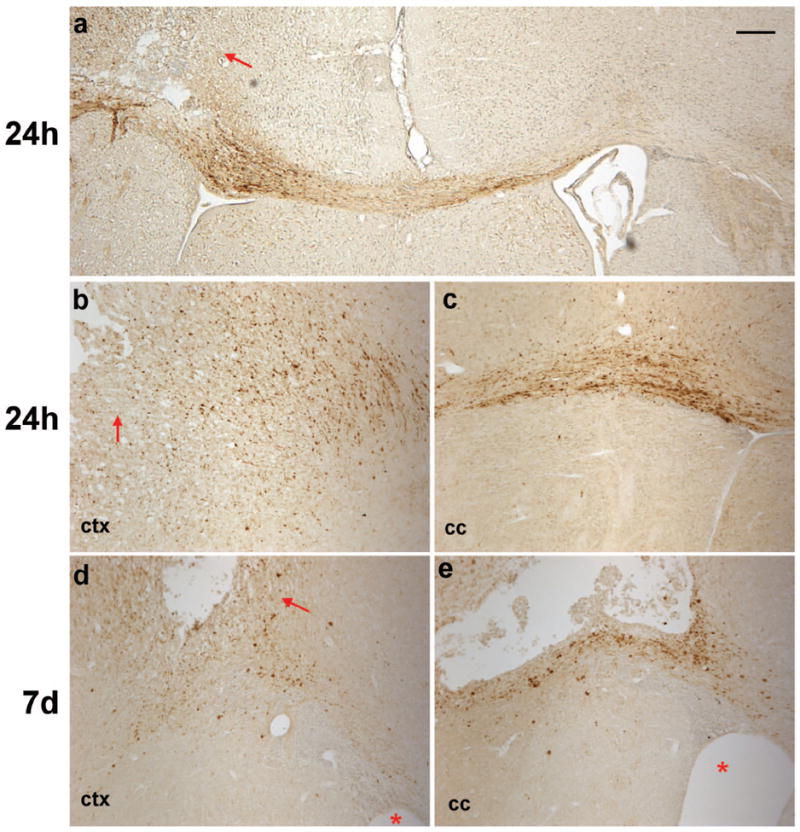
Axonal degeneration was detected by immuno-staining for β-APP accumulation after frontal TBI. Immuno-positive cells were abundant in the cortex at 24 h post-injury (a, b), particularly in the peri-contusional cortex (arrows). Filamentous staining was evident in the corpus callosum ipsilateral to the impact site at 24 h post-injury (a, c), indicating swollen or damaged axons in which β-APP was accumulating. This was most apparent directly ventral to the lesion site, however, immuno-reactive axons were also evident crossing the midline into the contralateral corpus callosum (a). At 7 d (d, e), much of the β-APP staining was granular or globular in appearance in the injured cortex and corpus callosum. Asterisks indicate ipsilateral ventricle. Scale bar =100 μm.
