Figure 1.
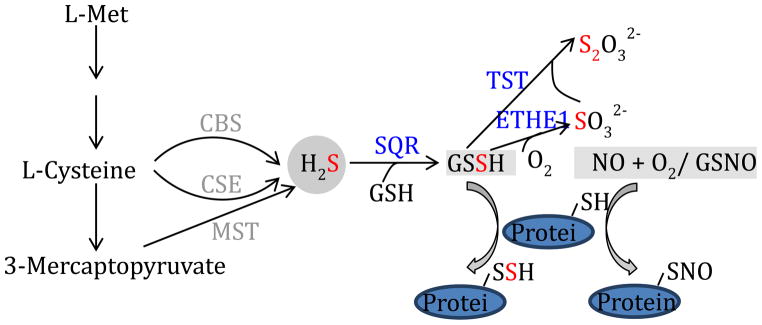
H2S biosynthesis and degradation, along with a comparison of pathways that contribute to protein S-sulfhydration and S-nitrosylation. The schematic depicts enzymatic pathways that are responsible for endogenous H2S production, formation of low-molecular-weight and proteinaceous persulfides and the mitochondrial pathway for persulfide degradation. Notably, in addition to endogenous mammalian enzymes, sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) of the colon are major contributors to H2S generation in vivo. Abbreviations: CSE, cystathionine γ-lyase; CBS, cystathionine β-synthase ; MST, mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase; SQR, sulfide quinone reductase; ETHE1, persulfide dioxygenase; TST, thiosulfate sulfur transferase (a.k.a. rhodanese).
