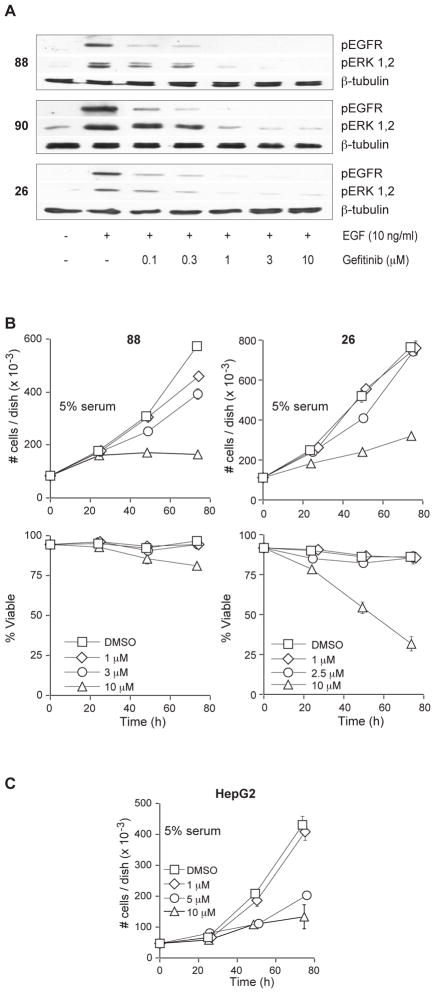
Figure 3.
Gefitinib inhibits EGF-stimulated activation of the EGFR-ERK pathway but does not inhibit MPNST proliferation. (A) Serum-starved cultures were treated with the indicated concentration of gefitinib (or vehicle) for 1 h, and subsequently treated with 10 ng/ml EGF for 10 min. EGFR and ERK activation were compared by immunoblotting with phospho-specific antibodies. β-tubulin was used as a total protein loading control. (B) Gefitinib does not inhibit the proliferation of MPNST lines at EGFR-selective concentrations. On day 0, plates were treated with either vehicle (DMSO) or the indicated concentration of gefitinib. Plates were harvested and cells counted at the indicated time-points and, the ability to exclude Trypan Blue was used to assess viability. These data show the effects of gefitinib on both total cell number (top panels) and percent viability (lower panels). Data represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent cultures for each line. (C) High concentrations of gefitinib have EGFR-independent effects. HepG2 cells were treated with either DMSO vehicle or the indicated concentration of gefitinib. Cells were harvested at the indicated time-points and counted using the Trypan Blue exclusion assay. Data represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent cultures.