Figure 4.
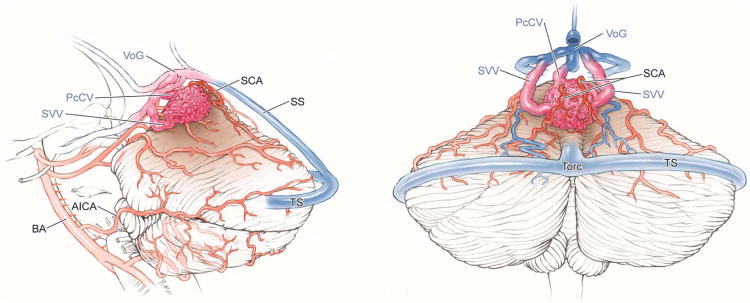
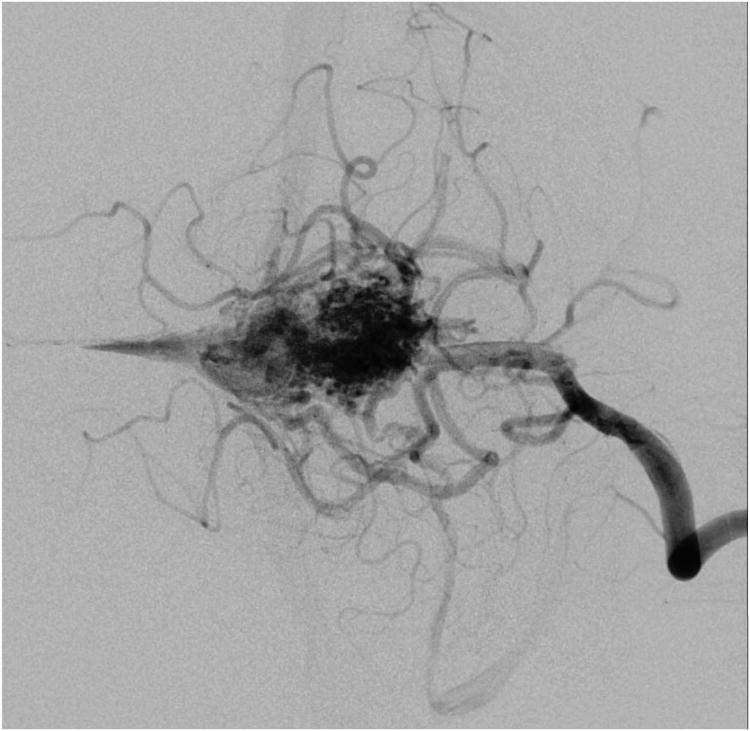
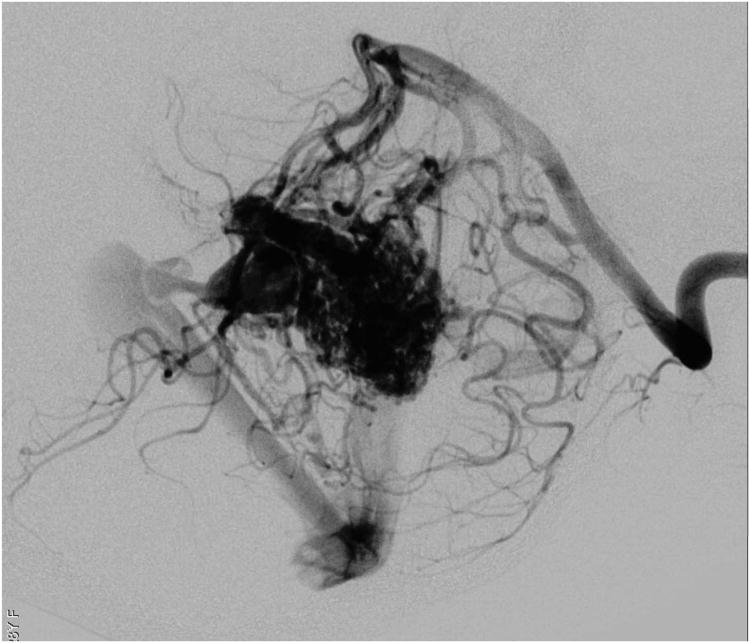
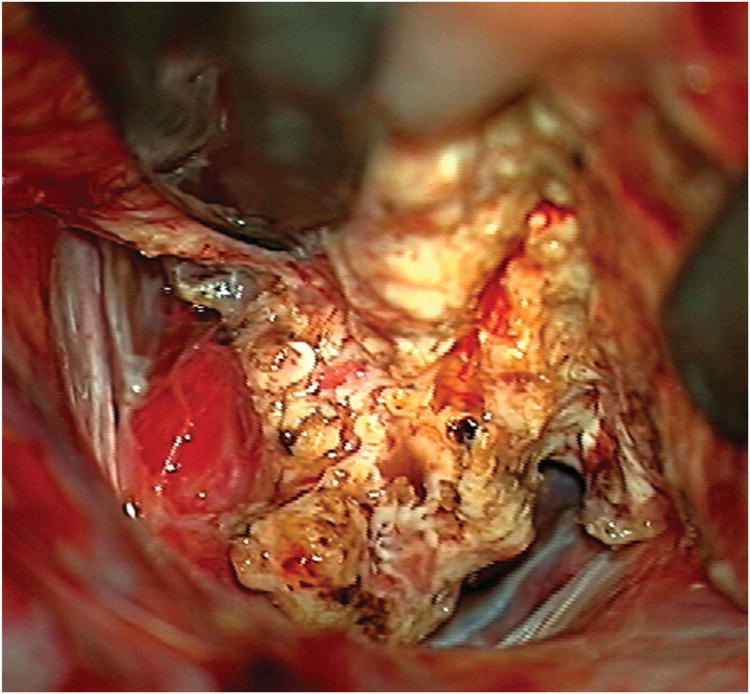
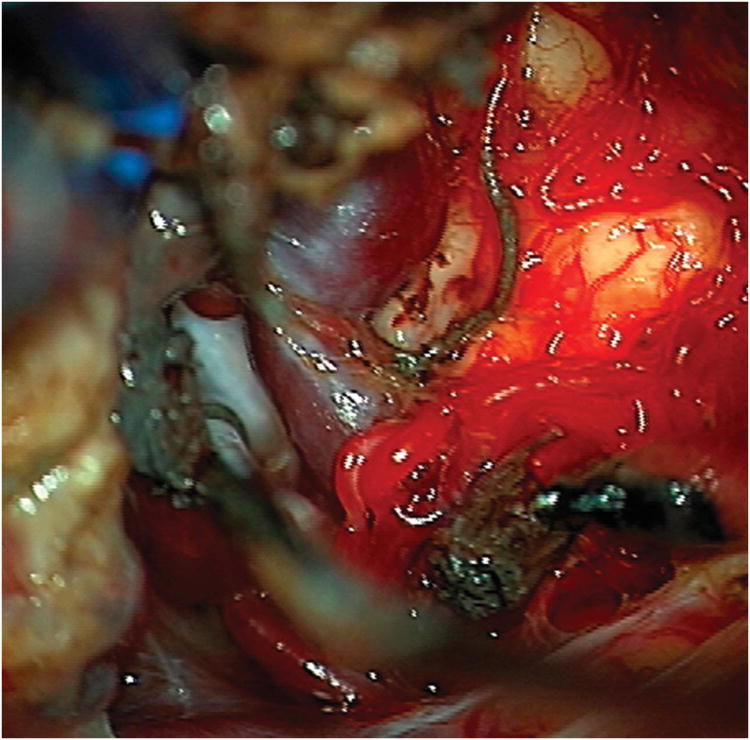
Cerebellar AVM, vermian subtype. The vermian AVM is midline and may be located on the suboccipital vermis or the tentorial vermis, as shown here in (A) left lateral and posterior views. The AVM is supplied by distal SCA branches bilaterally as they emerge from the cerebellomesencephalic fissure and course over the tentorial surface of the cerebellum. This vermian AVM in a 28 year-old woman (Spetzler-Martin grade III (S2V1E0), supplementary grade II (A2U0D0)) demonstrates bilateral supply from both SCAs, as seen on right vertebral artery digital subtraction angiography ((B) anteroposterior and (C) lateral views). Venous drainage into the precentral cerebellar vein/vein of Galen and the petrosal vein/superior petrosal sinus. (D) Torcular craniotomy in the prone position exposed the superior vermis, through which AVM was accessed. SCA feeding arteries were exposed under the tentorium, anterior to the nidus, and interrupted along the superior and lateral margins of the AVM. (E) The AVM remained attached to its ascending venous pedicle, which was traced to the vein of Galen. Abbreviations: BA = basilar artery; AICA = anterior inferior cerebellar artery; PICA = posterior inferior cerebellar artery; SS = straight sinus; TS = transverse sinus; SVV = superior vermian vein; PcCV = precentral cerebellar vein; VoG = vein of Galen; Torc = torcula.