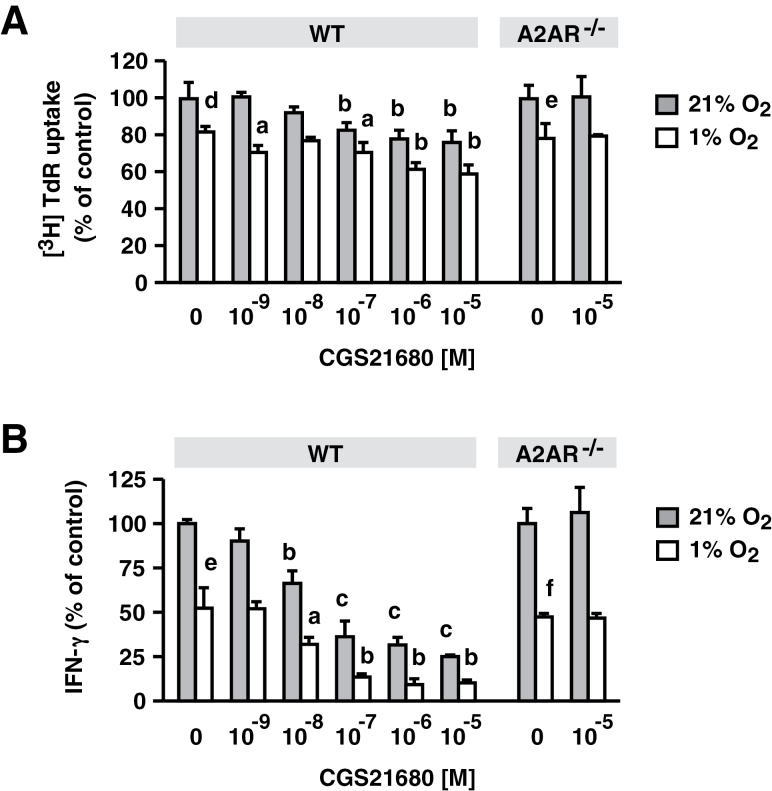
Fig. 1.
Suppression of T-cell functions by hypoxia did not require involvement of A2AR. Spleen cells from WT and A2AR−/− mice were stimulated with anti-CD3 mAb for 24h in the presence of various concentrations of CGS. Cell proliferative activity was monitored by [3H] thymidine uptake after 24h (A). IFN-γ levels in the supernatant were also determined after 24h (B). Hypoxia significantly inhibited cell proliferation and IFN-γ production in both WT and A2AR−/− T cells. Inhibition by CGS was observed only in WT cells. Data represent average ± SD of triplicate samples. a, P < 0.05; b, P < 0.01; c, P < 0.001 versus no CGS. d, P < 0.05; e, P < 0.01; f, P < 0.001; 21 versus 1% oxygen (no CGS).