Figure 1.
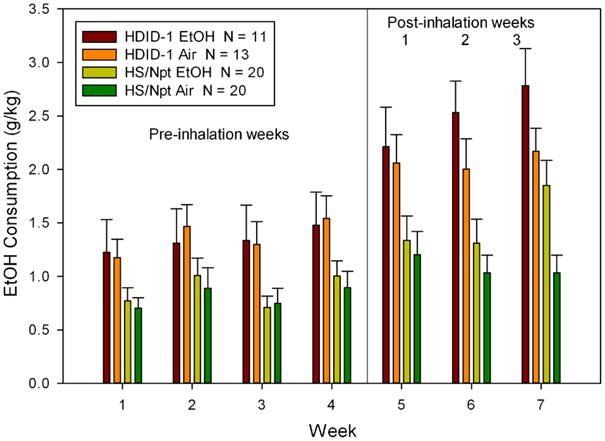
Chronic intermittent exposure to ethanol vapor increased ethanol drinking in both HDID-1 and HS mice as compared with air-exposed groups. Means ± standard errors intake during daily 2 hr sessions averaged over each 7-day period are shown for four weeks before ethanol vapor or air inhalation was initiated. Weeks 5-7 represent drinking averaged over the 5-day test period following each of the 3 cycles of four days of chronic intermittent vapor exposure.
