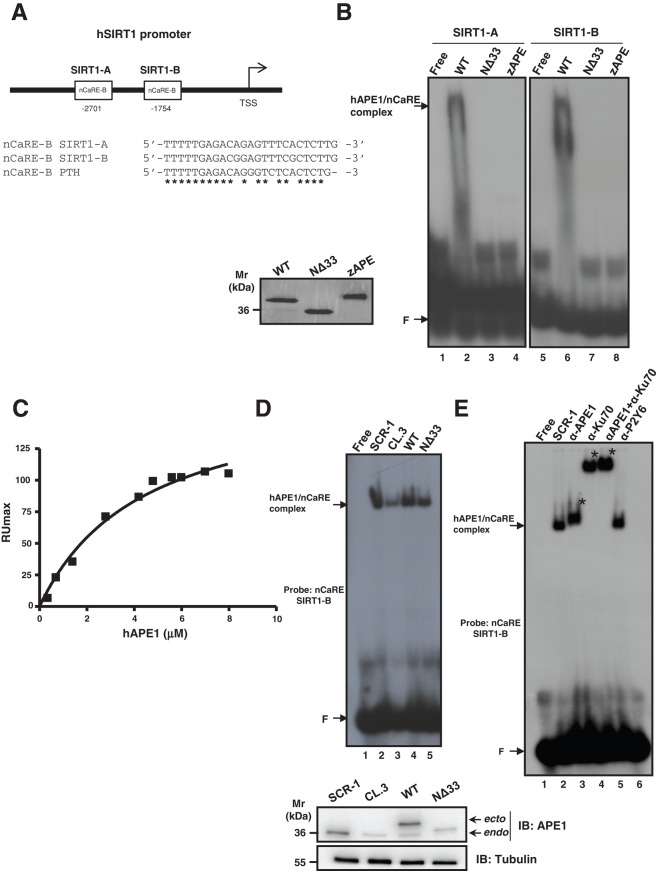
FIGURE 2:
APE1 is part of a nuclear protein complex that binds to the SIRT1 nCaRE sequence through its N-terminal domain. (A) Schematic representation (top) and multiple sequence alignment (bottom) of two nCaRE-B sequences found on the human SIRT1 gene promoter (SIRT1-A and SIRT1-B) with the nCaRE sequence found on the human PTH promoter (Okazaki et al., 1991). (B) EMSA analysis of nCaRE SIRT1-A and SIRT1-B sequence challenged with 10 pmol of purified APE1WT, APE1NΔ33, and zAPE1 proteins. Left, Coomassie staining of the purified recombinant proteins. (C) SPR analysis of the human APE1 (hAPE1)–nCaRE interaction. Recombinant hAPE1 and biotinylated nCaRE SIRT1-B (Table 1) were used as analyte and ligand, respectively. Plot of RUmax from each binding vs. hAPE1 concentrations (0.5–8 μM); data were fitted by nonlinear regression analysis. (D) Top, EMSA analysis of nCaRE SIRT1-B incubated with HeLa nuclear extract of different clones: control clone, APE1SCR-1 (lane 2), clone silenced for APE1, APE1CL.3 (lane 3), and clones reconstituted with APE1WT (lane 4) or APE1NΔ33 (lane 5). Bottom, Western blot analysis of APE1 protein in HeLa nuclear cell extracts. (E) EMSA analysis of nCaRE SIRT1-B with HeLa nuclear extract from APE1SCR-1 clone alone (lane 2) or preincubated with monoclonal antibody against APE1 (lane 3) or/and with an antibody against Ku-70 (lanes 4 and 5). Lane 6 corresponds to APE1SCR-1 nuclear extract incubated with a nonspecific antibody (α-P2Y6). Free indicates probe alone; F shows the position of the free oligonucleotide probe. Specific APE1/nCaRE interaction is indicated by the arrow. Asterisk indicates supershift.