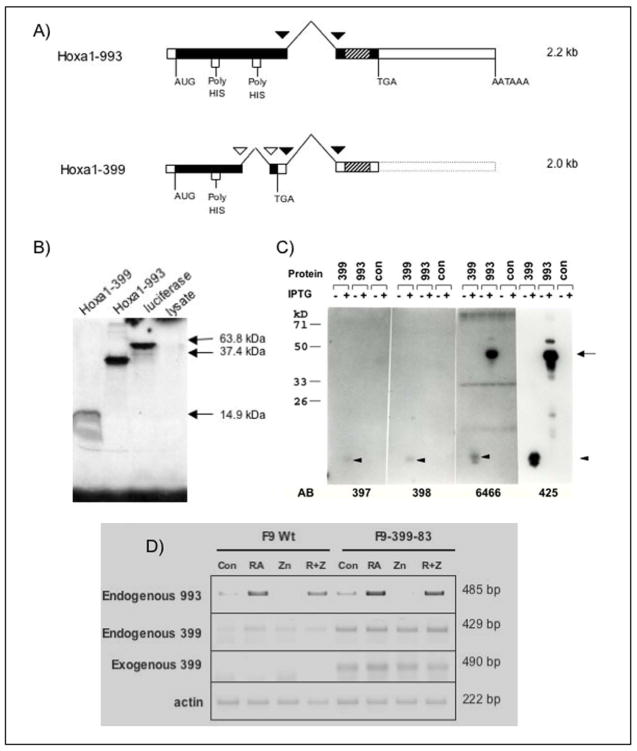
Figure 1. Splicing patterns of Hoxa1-993 and Hoxa1-399 cDNAs.
(A) Due to alternative splicing, two transcripts of Hoxa1 (previously Era-1) exist. Both transcripts share common splice sites, indicated by black triangles. However, Hoxa1-399 undergoes an additional splicing event, indicated by white triangles, causing a shift in the reading frame. This results in a truncated protein which lacks the homeodomain and a portion of the poly-His region that is present in Hoxa1-993. Hatched rectangles indicate the homeobox. (B) In vitro translated Hoxa1-993 and Hoxa1-399 detected by SDS-PAGE and subsequent radiography. Hoxa1-993 and Hoxa1-399 electrophoresed at the expected sizes of ~36 kDa and ~15 kDa, respectively. A luciferase expression construct was used as a positive control for the in vitro transcription and translation reaction. The luciferase protein electrophoresed at the expected size of 61 kDa. The rabbit reticulocyte lysate used for the in vitro transcription reaction was included as a negative control. (C) Hoxa1-993 and Hoxa1-399 proteins detected by western blot from IPTG-induced recombinant protein expressed in bacteria. The empty bacterial expression vector was included as a negative control. The primary antibodies used in these experiment were affinity-purified, polyclonal guinea pig or rabbit anti-mouse Hoxa1 antibodies. Antisera 6466 and 425 are specific to two different regions of the N-terminus of the Hoxa1 protein and recognize both Hoxa1-993 and Hoxa1-399. Antisera 397 and 398 are specific to the C-terminus of Hoxa1-399 and recognize Hoxa1-399 only. The proteins were immunoprecipitated with these antibodies and then electrophoresed. These experiments were performed at least two times with similar results. Arrow, expression of Hoxa1-993 protein; Arrowhead, expression of Hoxa1-399 protein. (D) RT-PCR analysis of exogenous and endogenous Hoxa1 transcripts in F9 Wt and F9-399-83 cells after 48 hr treatment with 1 μM RA and/or 100 μM ZnCl2. These assays were performed three times with similar results obtained.