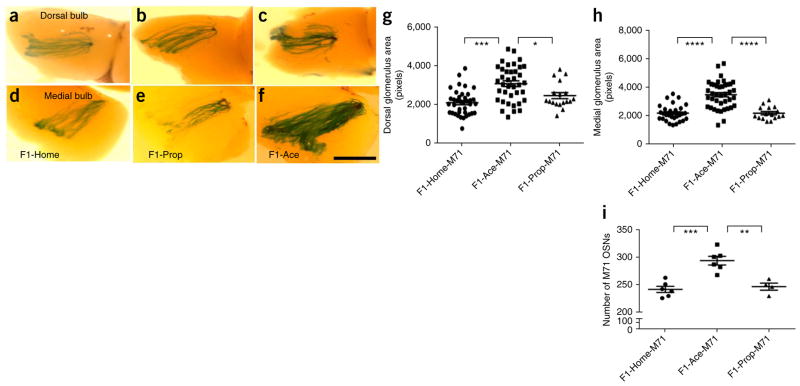
Figure 3.
Neuroanatomical characteristics of the olfactory system in F1 males after paternal F0 olfactory fear conditioning. (a–f) β-galactosidase staining revealed that offspring of F0 males trained to acetophenone (F1-Ace-M71) had larger dorsal and medial acetophenone-responding glomeruli (M71 glomeruli) in the olfactory bulb compared with F1-Prop-M71 and F1-Home-M71 mice. Scale bar represents 1 mm. (g) Dorsal M71 glomerular area in F1 generation (M71-LacZ: F1-Home, n = 38; F1-Ace, n = 38; F1-Prop, n = 18; ANOVA, P < 0.0001, F2,91 = 15.53; F1-Home-M71 versus F1-Ace-M71, P < 0.0001; F1-Ace-M71 versus F1-Prop-M71, P < 0.05). (h) Medial M71 glomerular area in F1 generation (M71-LacZ: F1-Home, n = 31; F1-Ace, n = 40; F1-Prop, n = 16; ANOVA, P < 0.0001, F2,84 = 31.68; F1-Home-M71 versus F1-Ace-M71, P < 0.0001; F1-Ace-M71 versus F1-Prop-M71, P < 0.0001). (i) F1-Ace-M71 mice had a larger number of M71 OSNs in the MOE than F1-Prop-M71 and F1-Home-M71 mice (M71-LacZ: F1-Home, n = 6; F1-Ace, n = 6; F1-Prop, n = 4; ANOVA, P = 0.0001, F2,13 = 18.80; F1-Home-M71 versus F1-Ace-M71, P < 0.001; F1-Ace-M71 versus F1-Prop-M71, P < 0.01). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.