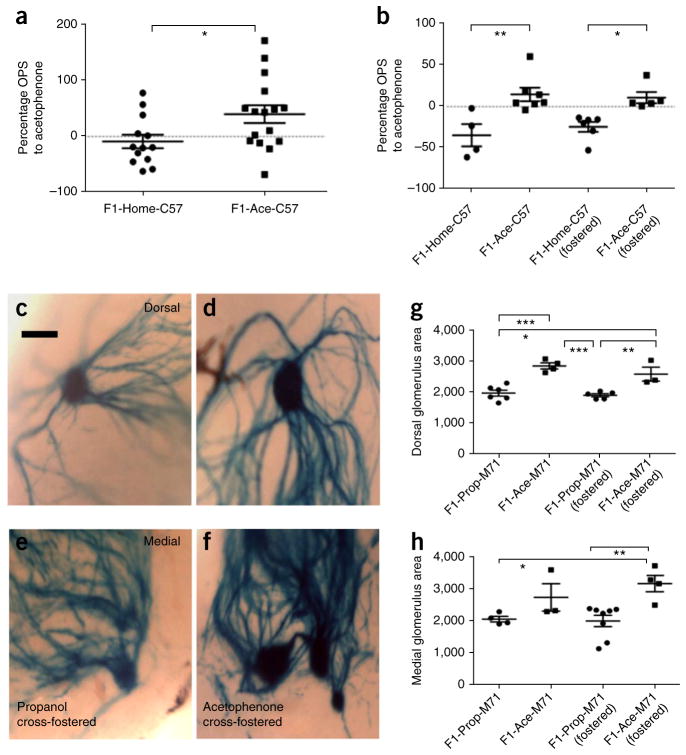
Figure 5.
Behavioral sensitivity and neuroanatomical changes persist after cross-fostering. (a) F1 offspring of mothers that had been fear conditioned with acetophenone (F1-Ace-C57) showed enhanced sensitivity to acetophenone compared with F1-Home-C57 controls (F1-Home-C57, n = 13; F1-Ace-C57, n = 16; t test, P = 0.0256, t27 = 2.362). (b) Cross-fostering behavior. F1-Ace-C57 males had higher OPS to acetophenone than F1-Home-C57 males (P < 0.01). F1-Ace- C57(fostered) males still had higher OPS to acetophenone than F1-Home-C57(fostered) males (P < 0.05) (ANOVA, P = 0.0011, F3,18 = 6.874, planned post hoc comparisons). (c–f) Cross-fostering neuroanatomy. F1-Ace- M71 males cross-fostered by mothers conditioned to propanol (F1-Ace-M71(fostered)) continued to have larger M71 glomeruli than F1-Prop-M71 males cross-fostered by mothers conditioned to acetophenone (F1-Prop-M71(fostered)). Scale bar represents 100 μm. (g) Dorsal M71 glomerular area in F1 cross-fostered generation (M71-LacZ: F1-Prop, n = 6; F1-Ace, n = 4; F1- Prop(fostered), n = 5; F1-Ace(fostered), n = 3; ANOVA, P < 0.0001, F3,14 = 17.52; F1-Prop versus F1-Ace, P < 0.001; F1-Prop(fostered) versus F1-Ace(fostered), P < 0.01). (h) Medial M71 glomerular area in F1 cross-fostered generation (M71-LacZ: F1-Prop, n = 4; F1-Ace, n = 3; F1-Prop(fostered), n = 8; F1-Ace(fostered), n = 4; ANOVA, P < 0.01, F3,15 = 5.933; F1-Prop (fostered) versus F1-Ace(fostered), P < 0.01). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.