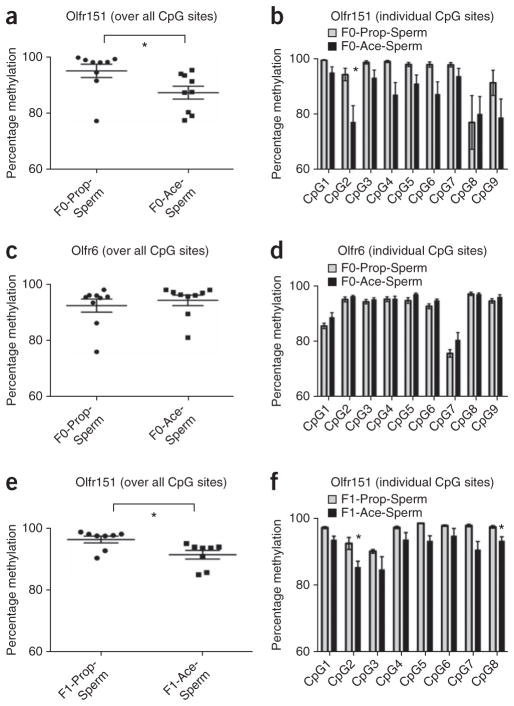
Figure 6.
Methylation of odorant receptor genes in sperm DNA from conditioned F0 and odor naive F1 males. (a) Bisulfite sequencing of CpG di-nucleotides in the Olfr151 (M71) gene in F0 sperm revealed that F0-Ace mouse DNA (n = 12) was hypomethylated compared with that of F0-Prop mice (n = 10) (t test, P = 0.0323, t16 = 2.344). (b) A particular CpG di-nucleotide in the Olfr151 (M71) gene in F0 sperm was hypomethylated in F0-Ace mice (n = 12) compared with F0-Prop mice (n = 10) (P = 0.003, Bonferroni corrected). (c) We found no differences in methylation between F0-Ace (n = 12) and F0-Prop (n = 10) mice across all of the CpG di-nucleotides queried in the Olfr6 gene in F0 sperm (P > 0.05). (d) Across specific CpG di-nucleotides in the Olfr6 gene, we found no differences in methylation between F0-Ace (n = 12) and F0-Prop (n = 10) mice (Bonferroni corrected). (e) Bisulfite sequencing of the Olfr151 (M71) gene in F1 sperm revealed that F1-Ace mouse DNA (n = 4) was hypomethylated compared with that of F1-Prop mice (n = 4) (t test, P = 0.0153, t14 = 2.763). (f) Bisulfite sequencing of CpG di-nucleotides in the Olfr151 (M71) gene in F1 sperm revealed that two particular CpG di-nucleotides in the Olfr151 (M71) gene were hypomethylated in F1-Ace mice (n = 4) compared with F1-Prop mice (n = 4) (P = 0.002, Bonferroni corrected). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05 after correction.