Figure 3.
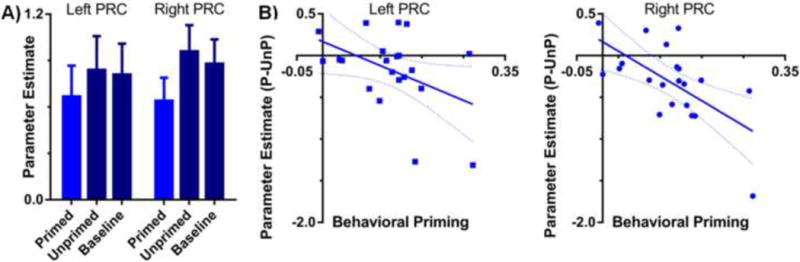
ROI-based analysis of PRC activity related to conceptual implicit memory. (A) Average parameter estimates from the PRC ROIs for primed, unprimed, and baseline trials from the free association priming task. There were activity reductions in the PRC for primed relative to both unprimed and baseline targets (ps < .05). Error bars reflect the SEM. (B) The relationship between the difference in activity for primed (P) and unprimed (UnP) targets in the PRC ROIs and the magnitude of the behavioral priming effects (i.e., the proportion of baseline targets produced relative to the proportion of studied targets produced) in the free association task. Neural priming in PRC was correlated with greater conceptual priming in both hemispheres (ps < 0.05). Dashed lines reflect the 95% CI.
