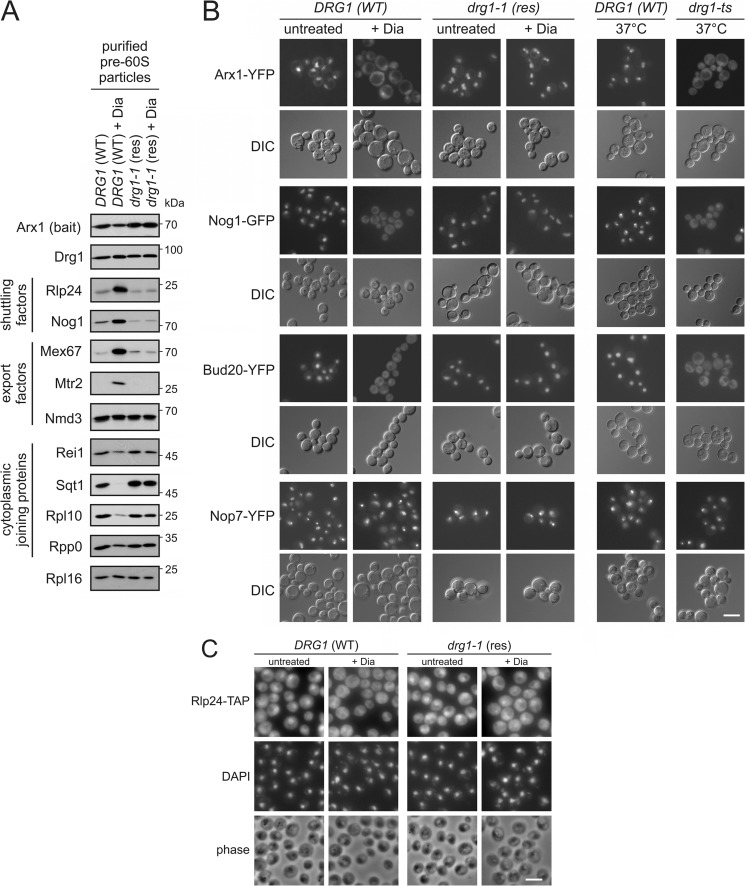
FIGURE 1.
Diazaborine blocks maturation of late pre-60S particles. A, diazaborine treatment leads to the enrichment of shuttling and export factors in purifications of late pre-60S particles. The DRG1 wild-type strain (DRG1 (WT)) and the diazaborine resistant drg1-1 mutant (drg1-1 (res)) were treated with 370 μm diazaborine for 1 h. Afterward pre-60S particles were isolated with Arx1-TAP as bait protein and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies directed against shuttling proteins, export factors, and late joining cytoplasmic factors. B, diazaborine (Dia) triggers the cytoplasmic accumulation of shuttling factors. Yeast strains expressing chromosomal fusions of shuttling pre-60S maturation factors Arx1, Nog1, or Bud20 with YFP or GFP in the DRG1 wild-type (DRG1 (WT)) and the diazaborine resistant drg1-1 mutant (drg1-1 (res)) were treated with diazaborine. After 1 h, samples were inspected by fluorescence microscopy. A strain expressing a chromosomal fusion of the strictly nuclear pre-60S maturation factor Nop7 with YFP was used as a control. As a control for cytoplasmic accumulation, the localization of the respective fluorescent proteins was also inspected in the drg1-ts background. DIC, differential interference contrast picture. C, the shuttling factor Rlp24 accumulates in the cytoplasm after treatment with diazaborine. Immune fluorescence with TAP-tagged Rlp24 is shown. The DRG1 wild-type strain (DRG1 (WT)) or the diazaborine-resistant drg1-1 mutant (drg1-1 (res)) expressing Rlp24-TAP fusion proteins were treated with diazaborine for 1 h. Thereafter cells were fixed, and Rlp24-TAP was detected by immunofluorescence. DAPI, DAPI staining of the DNA in the nucleus. Phase, phase contrast pictures to monitor morphological integrity of the cells. White scale bars in B and C, 5 μm.