FIGURE 1.
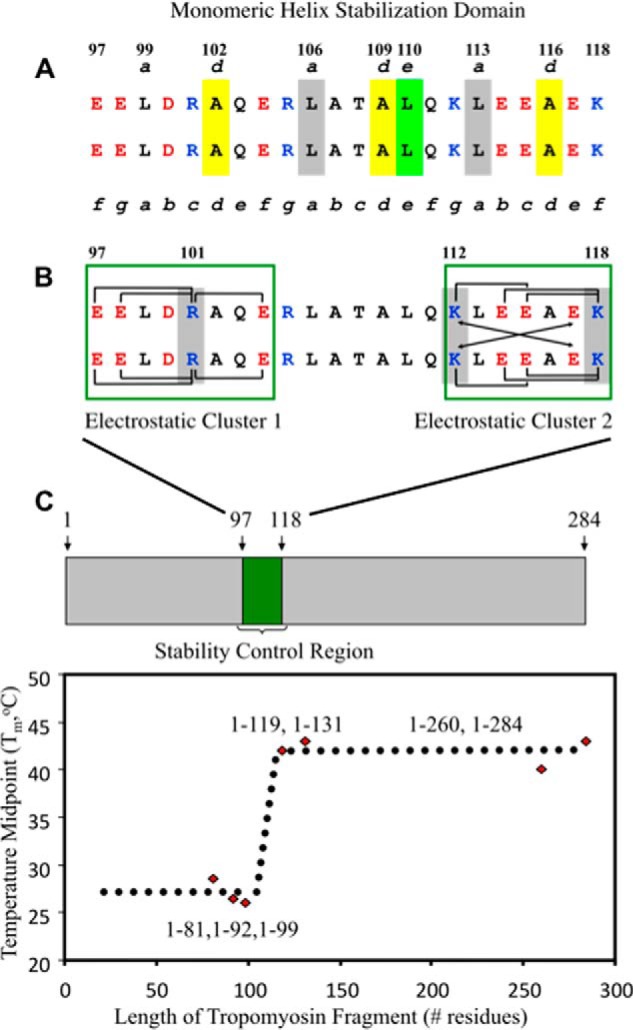
The stability control region of tropomyosin and its critical interactions. The Tm sequence 97–118 includes all of the electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions that comprise the stability control region in α-tropomyosin (78). Shown in A is the monomeric helix stabilization domain, which consists of yellow-shaded Ala residues that occupy three consecutive d positions (102, 109, 116) in this region and Ala-109d to Leu-110e (shaded in yellow and light green, respectively) that promote a novel packing arrangement between Leu-106a (gray), Leu-110e (light green), and Leu-113a (gray) (78) within the monomeric helix stabilization domain. In B, green boxes outline electrostatic clusters 1 and 2, with a large number of intrachain and interchain ionic attractions. The brackets denote i to i + 3 and i to i + 4 intrachain electrostatic attractions. The arrows denote i to i′ + 5 interchain electrostatic attractions (g–e′ and g′–e). Arg-101c, Lys-112g, and Lys-118f are critical to the electrostatic clusters and are shaded in gray. The stability control region was identified from circular dichroism temperature unfolding experiments of tropomyosin C-terminal deletion fragments that showed a 15 °C increase in the TM (temperature midpoint) value of fragment 1–119 compared with fragment 1–99 (C shows the plot of TM values versus tropomyosin fragment length) (77).
