FIGURE 5.
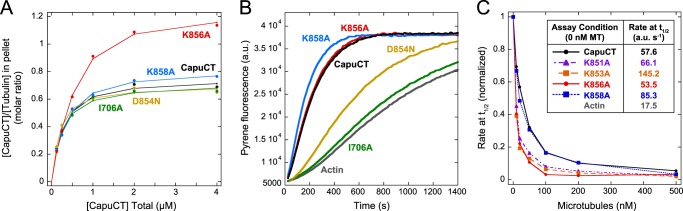
FH2 domain residues contribute to microtubule binding. A, microtubule binding by CapuCT-I706A, -D854N, -K858A, -K856A, and wild-type at 50 mm KCl with 0.5 μm tubulin. B, actin polymerization activity of 10 nm each CapuCT FH2 mutant. C, CapuCT-K856A, but not CapuCT-K858A, is more sensitive to microtubule inhibition than wild-type CapuCT. Two additional FH2 mutants, CapuCT-K851A and CapuCT-K853A, also exhibited increased sensitivity to microtubule inhibition. For each construct, 10 nm was used and rates at the time until half-maximal polymerization (t½) were normalized to the maximum polymerization rate (0 nm microtubules (MT)) and the baseline polymerization rate (actin) were reported in the Table inset (a.u., arbitrary units).
