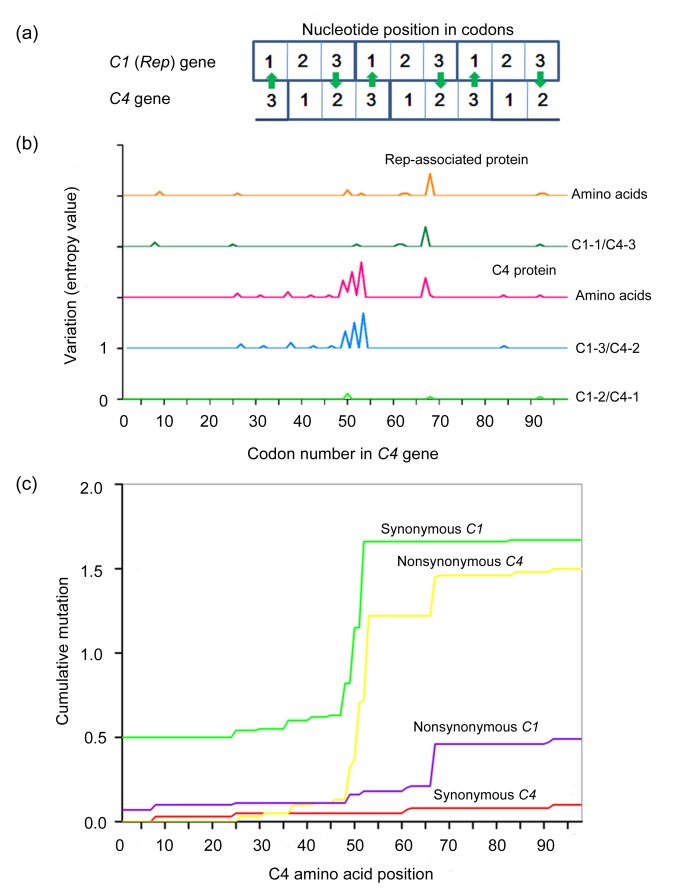
Fig. 3.
Variation in nucleotides and amino acids of the overlapping C1 and C4 genes
(a) Frame-shifted positions of the overlapping C1 and C4 genes. Mutations in the open reading frames of the overlapping C1 and C4 genes result in differential rates of amino acid changes. For example, a nucleotide mutation in the third position of the C1 codon is likely to be synonymous, allowing a nonsynonymous mutation in the C4 codon (arrows). (b) Levels of nucleotide and amino acid variation in the three sets of nucleotides in relation to the nucleotide positions of the codons in the overlapping Rep and C4 proteins. (c) Cumulative incidences of synonymous and nonsynonymous mutations in the overlapping region of C1/C4. The x axis represents the position of the codon in C4, and the y axis represents the cumulative values of synonymous or nonsynonymous mutations estimated at a specific codon position