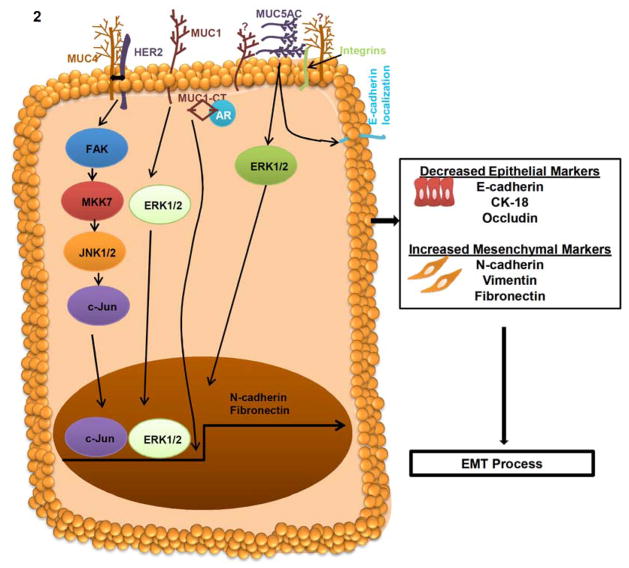
Fig. 2. Mechanism of MUC4, MUC1 and MUC5AC mucins in EMT process.
In cancer cells, MUC4 interacts with HER2 and subsequently activates FAK/MKK7/JNK and c-Jun to regulate the N-cadherin expression. MUC4 dependent up-regulation of N-cadherin involved in the cellular alteration of EMT in pancreatic, ovarian and breast cancer cells. MUC4 induced EMT increase the expression of mesenchymal markers N-cadherin and Vimentin as well as decrease the expression of epithelial markers E-cadherin, CK-18 and Occludin. MUC1 activates ERK1/2 and leads to the regulation of Fibronectin for EMT process. Furthermore, the cytoplasmic tail (CT) of MUC1 interacts with the DNA binding domain of androgen receptor (AR) and resulted in the activation of EMT process and invasiveness of cancer cells. MUC5AC, a secretory mucin involved in differential localization of E-cadherin and ERK1/2 activation for the EMT process.