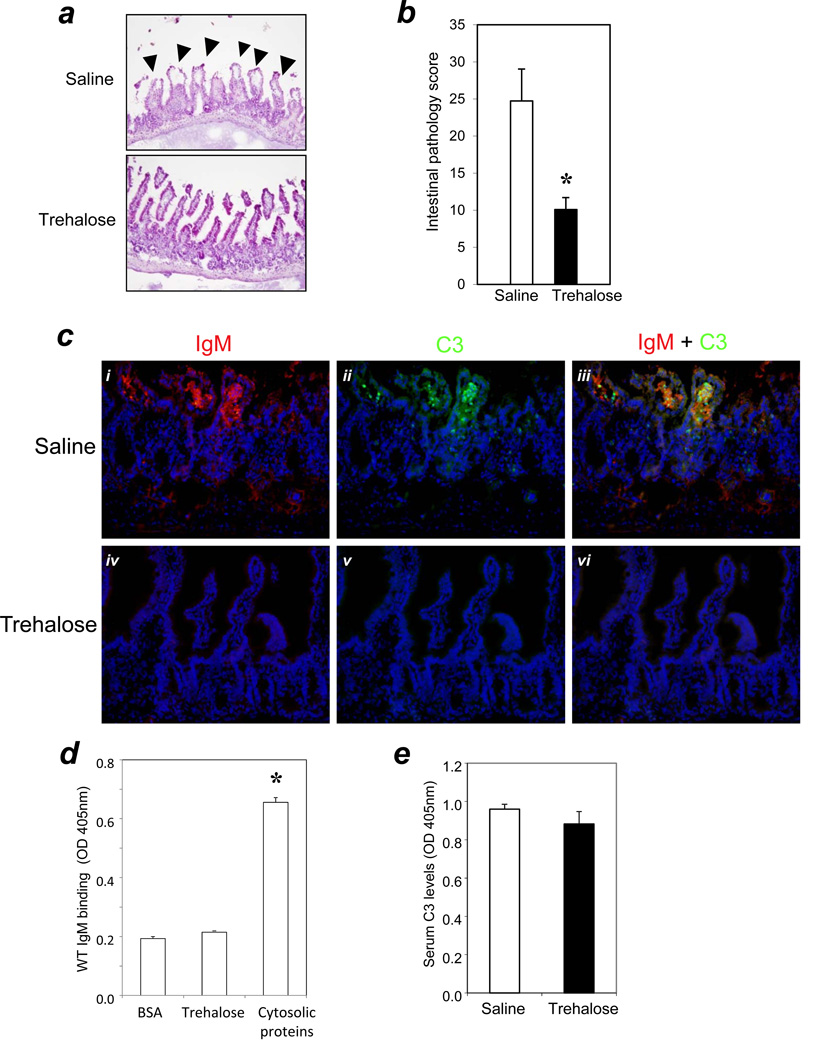
Figure 2. Cell membrane stabilization reduced tissue damage and blocked IgM-mediated complement response in the intestinal I/R.
(a) Trehalose or saline were administered i.p. at a dose of 1g/kg to WT mice 30 minutes prior to I/R surgery (n=11/group). H&E staining was performed as described in Methods. Arrows indicate typical pathology features of villi injury (200× magnification). (b) Bar graph: bars indicate pathology scores. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (P<0.01). (c) Trehalose treatment blocks the deposition of IgM/C3 in WT mice. Cryosections were prepared following I/R and analyzed for IgM (panels i & iv) and C3 deposition (panels ii & v). Panels iii and vi are merged images of (i + ii) and iv + v), respectively. Panels i-iii: WT mice received saline; panels iv-vi: WT mice received trehalose. Sections were stained as in Figure 1 (200 × magnification). (d) IgM does not bind specifically to trehalose. ELISAs were performed in triplicate as described in Methods. The binding of IgM to BSA served as a negative control; the binding of IgM to the cytosolic protein fraction of naive WT mouse served as a positive control. * indicated that IgM binding to the cytosolic proteins was significantly higher (P < 0.05) than IgM binding to either BSA or trehalose. (e) Trehalose treatment did not change the systemic C3 levels in mice. Serum complement C3 levels in mice with or without trehalose treatment (n=11/group) were measured by ELISA as described in Methods.