Figure 2.1.
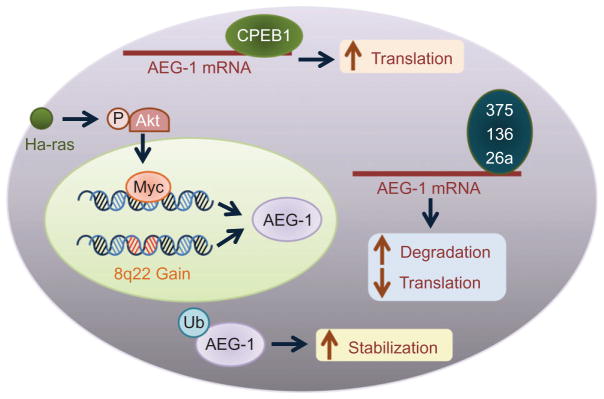
Molecular mechanism of AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC overexpression in cancer. Genomic amplification (8q22 gain) leading to increased AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC expression has been documented in breast and liver cancers. Activation of Ha-ras results in activation of PI3K/Akt and subsequent binding of c-Myc to AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC promoter increasing transcription. Monoubiquitination of AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC protein in cancer cells leads to increased stabilization and cytoplasmic accumulation. AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC mRNA is posttranscriptionally regulated by several tumor suppressor mRNAs, such as miR-375, miR-136, and miR-26a, which are downregulated in multiple cancers. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 1 (CEBP1) binds to the 3′-UTR of AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC mRNA and promotes its translation in glioma cells.
