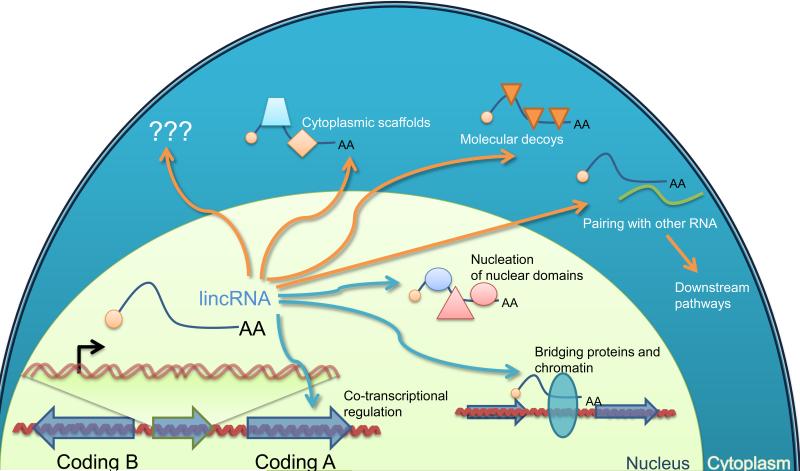
Figure 5. Diverse Mechanisms Proposed for lincRNA Function.
Modes of action include cotranscriptional regulation (e.g., through either the interaction of factors with the nascent lincRNA transcript or the act of transcribing through a regulatory region), regulation of gene expression in cis or in trans through recruitment of proteins or molecular complexes to specific loci, scaffolding of nuclear or cytoplasmic complexes, titration of RNA-binding factors, and pairing with other RNAs to trigger posttranscriptional regulation. The two latter mechanisms are illustrated in the cytoplasm (where they are more frequently reported) but could also occur in the nucleus. Additional mechanisms will presumably be proposed as additional functions of lincRNAs are discovered.