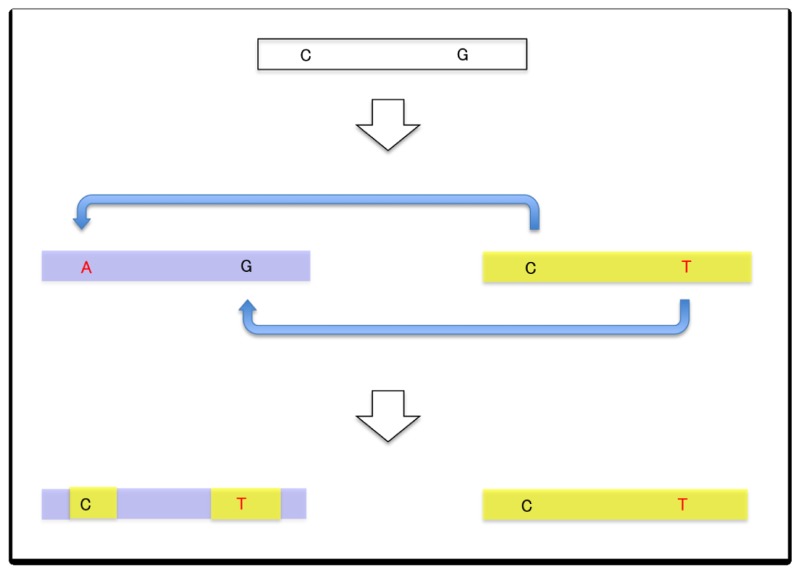
Figure 1.
Simple gene conversion model for a pair of duplicated genes (or paralogous genes). Converted tracts will be pasted to the corresponding part of the paralog, while there is no change in the original gene. Conversion can result in the novel mutation (shown in red) being spread or reversed. Although converted tracts will become identical in sequence, conversion will create novel haplotypes that are chimeras of the two genes (shown in purple and yellow).