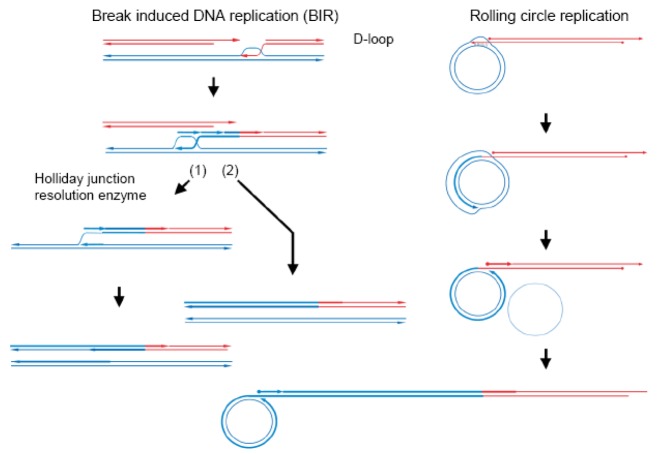
Figure 2.
Double-stranded break-induced DNA replication (BIR) and rolling circle DNA replication. Steps after homologous pairing (D-loop formation; see Figure 1) are indicated. In pathway (1), the crossed strands are cleaved and a replication fork is formed, and then authentic DNA replication occurs. In pathway (2), the D-loop moves along with strand synthesis, followed by lagging strand synthesis. When the donor DNA is circular, the D-loop formation initiates rolling circle replication. Bold lines indicate newly synthesized strands. Red DNA alleles are either lost by double-stranded break-induced DNA replication, or extensively decreased within a multicopy DNA population by rolling circle replication.