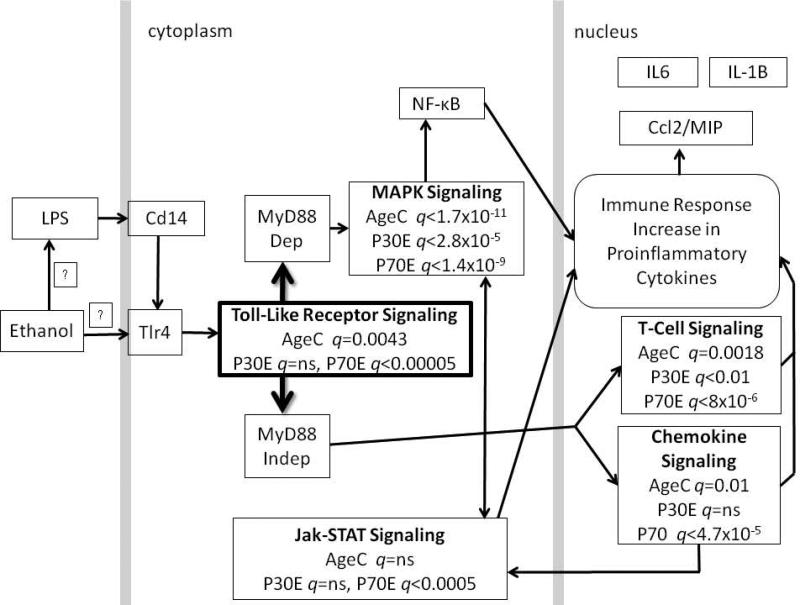
Figure 2.
Pathway analysis of alcohol-induced gene expression revealed significant over-representation of immune pathways predominantly in adult mice, with little or no significance in the adolescents. Various biological pathways that directly or indirectly have a role in immune response signaling are shown, with the false discovery rate (FDR) protected significance (q < 0.05) value for both age groups stated for each pathway. Three unbiased WebGestalt (Zhang et al., 2005) analyses were used to determine pathway differences in age- and alcohol-related brain transcriptome changes (AgeC = comparison between adolescent and adult controls, P30E = adolescent control compared to adolescent ethanol drinking, P70E = adult control compared to adult ethanol drinking). The cartoon was generated based on potential mechanisms, as determined in silico, that may influence binge alcohol consumption. Arrows indicate direction of response with initial Tlr4 action leading to either MyD88 dependent or independent downstream changes. It is unknown how alcohol directly acts on neuroimmune function, yet genetic and functional studies have shown a role for LPS, Cd14 and Tlr4. Therefore, a boxed “?” is used to depict possible action. Mechanisms known to occur in the cytoplasm and nucleus are shown in their respective compartments divided by gray bars. However, although action is likely to predominantly occur via microglia, cell specificity remains to be determined in future studies. Abbreviations are: Ccl2/MIP, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 / macrophage inflammatory protein; Cd14, monocyte differentiation antigen Cd14; IL-1B, interleukin 1 beta; IL6, interleukin 6; Jak-STAT, Janus kinase - signal transducer and activator of transcription; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells; Tlr4, Toll-like receptor 4.