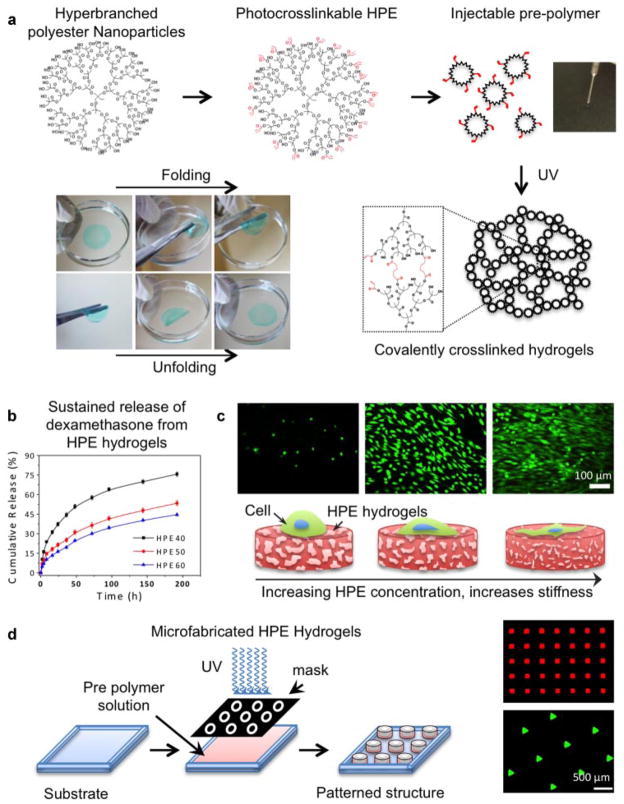
Figure 4.
Nanocomposite hydrogels from hyperbranched polyester (HPE) nanoparticles. a: HPE nanoparticles are surface functionalized with photocrosslinkable moieties. When the precursor solution containing functionalized HPE and photoinitiator is subjected to UV radiation, a covalently crosslinked network is obtained. This covalently crosslinked hydrogel is mechanically stable and can maintain its shape in physiological conditions. b: Due to the presence of hydrophobic cavities within the HPE nanoparticles, hydrophobic drugs such as dexamethasone can be entrapped. A sustain release of drug from the hydrogels network was observed over a week. c: By controlling the crosslinking density of the HPE hydrogels, physical properties and cell adhesion characteristics can be tuned. d: Photolithography technique can be used to fabricated micropatterned hydrogel structure to control the cellular interactions. Adapted with permission from Zhang et al. (2013). Copyright (2011) American Chemical Society.