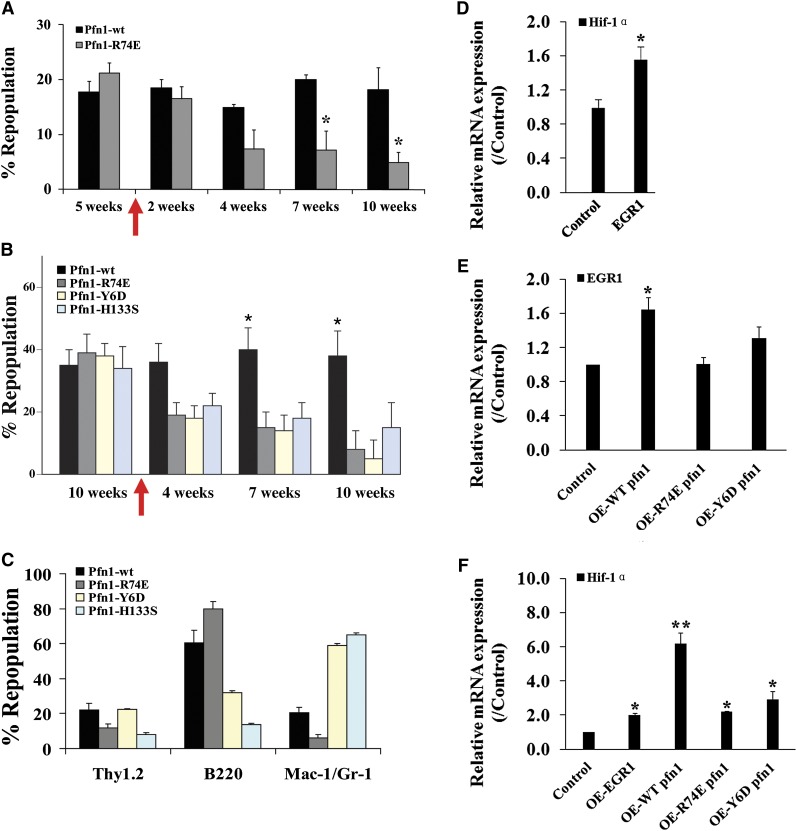
Figure 6.
Actin and poly-proline binding is critical to pfn1’s function in HSCs. (A-B) E16 fetal liver Sclpfn1 Lin− cells were infected with retrovirus encoding WT, actin binding–deficient pfn1, or poly-proline-binding–deficient pfn1 and were then transplanted into lethally irradiated CD45.1 recipients. Five to 10 weeks later, the mice were treated with tamoxifen for 2 weeks. Donor engraftment at indicated time after transplant is shown (n = 5). (C) Multilineage contribution of donor cells in recipients at 10 or 15 weeks after transplant (n = 5). (D) Control or EGR1 retrovirally expressed Sclpfn1 BM cells were transplanted into CD45.1 recipients with competitors. Mice were treated with tamoxifen after 5 weeks. Donor-derived CD45.2+ LSK cells were sorted, and expression of Hif-1α was measured (n = 3). (E) Pfn1 or Pfn1 mutants were retrovially expressed in WT LSK cells, and expression of EGR1 was measured (n = 3). (F) Pfn1, Pfn1 mutants, or EGR1 was retrovially expressed in WT LSK cells, and expression of Hif-1α was measured (n = 3). *P < .05, different from control values; **P < .05, different from mutant pfn1 values.