Table 2. Analysis of the effect of covariates on survival of oysters in the Thau lagoon by a Cox proportional hazards model.
| Covariate | Hazardratio | Hazardratio SE |
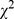
|
p value |
| Areas | n.a | n.a | 33.2 | <0.001 |
| Bouzigues vs Outside | 9.671 | 4.282 | 26.3 | <0.001 |
| Mèze vs outside | 14.870 | 6.975 | 33.1 | <0.001 |
| Marseillan vs outside | 13.551 | 6.876 | 26.4 | <0.001 |
| Marseillan vs Mèze | 0.911 | 0.228 | 0.1 | 0.710 |
| Marseillan vs Bouzigues | 1.401 | 0.870 | 1.9 | 0.165 |
| Mèze vs Bouzigues | 1.537 | 0.346 | 3.7 | 0.056 |
| OsHV-1 DNA | 1.405 | 0.209 | 5.2 | 0.022 |
| Triacylglycerol | 0.971 | 0.018 | 2.4 | 0.119 |
| Carbohydrate | 1.004 | 0.002 | 3.3 | 0.070 |
| Δ Triacylglycerol | 0.771 | 0.082 | 6.0 | 0.014 |
| Δ Carbohydrate | 0.680 | 0.108 | 5.9 | 0.015 |
For each covariate, the following elements are provided: its parameter estimate and the corresponding instantaneous hazard ratio and its standard error (SE); the χ2 statistic (with 1 degree of freedom for all tests except for areas where it was 3) and the resulting p value for the type II test from the complete model. Covariates are the presence or not of OsHV-1 DNA in oysters (on 6 April), their triacylglycerol and carbohydrate reserves (on 6 April), and the relative variation of these energetic reserves (Δ) between 6 and 16 April.
