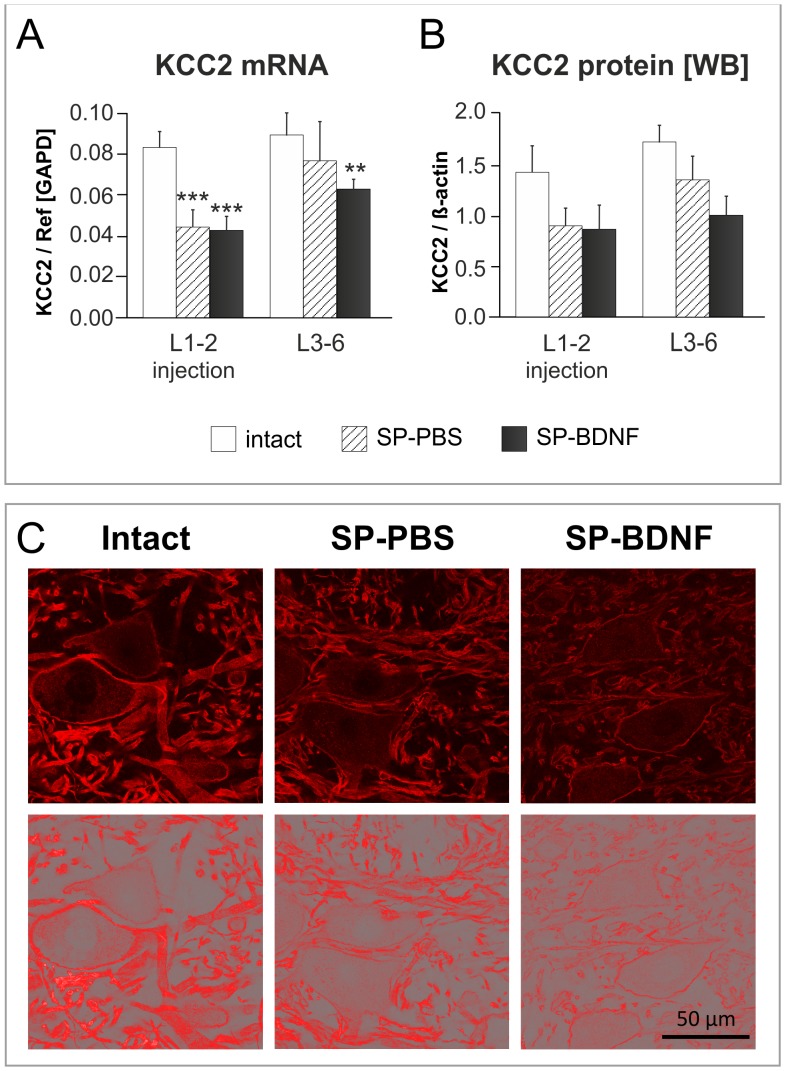
Figure 7. Effect of spinal cord transection and BDNF overexpression on segmental potassium-chloride co-transporter 2 (KCC2) transcript and protein level.
(A) Spinal cord transection leads to a significant decrease in KCC2 mRNA level in L1–2 segments (hatched bars). In SP-BDNF rats KCC2 mRNA is equally reduced in L1–2 segments and tends to be lower in L3–6 segments than in SP-PBS rats (black bars). (B) Similar tendencies were observed at the protein level. Data are the means ± SD (qPCR) or means ± SEM (WB) from 5 intact, 3 SP-PBS and 4 SP-BDNF rats. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc tests were used; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (C) The representative confocal microscopy images (upper panel) and the same images tresholded (lower panel) show the pattern and intensity of KCC2 immunostaining of large diameter neurons and surrounding neuropil in the ventral horn of the spinal cord of the rats from intact, SP-PBS and SP-BDNF groups. Note a remarkable reduction of KCC2 labeling in both spinalized groups, with a loss of continuity of the cell membrane signal and torn up appearance of the processes.