Table 2.
1H and 13C chemical shifts in the anomeric region characteristic for the RO-LMWHs
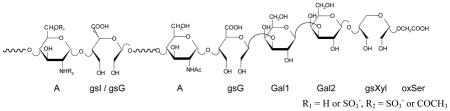 R1 = H or SO3−, R2 = SO3− or COCH3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| RESIDUE | 1H, ppm | 13C, ppm |
| Aminosugars | ||
| ANAc-(gsG)a | 5.09 | 99.0 |
| ANAc-(gsI)b | 5.12 | 98.0 |
| ANS-(gsI)c | 5.39 | 99.8 |
| ANS-(R)d | 5.34 | 99.2 |
| Glycol-split uronic acids | ||
| gsG-(ANAc)a | 4.71 | 106.7 |
| gsI-(ANAc)b | 4.94 | 106.9 |
| gsI-(ANS)c | 4.98 | 106.9 |
| gsG (RO-heparinse and RO-tinzaparin) | 4.87 | 106.4 |
| gsG (RO-LMWHs)f | 4.80 | 106.5 |
| gsIe | 4.98 | 106.9 |
| gsU-(A*)g | 4.90 | 103.2 |
| Residues of the gsLR | ||
| gsG-(Gal1) = gsGLR | 4.92 | 107.6 |
| Gal1 | 4.66 | 106.9 |
| Gal2 | 4.61 | 105.0 |
| gsXyl | 4.75 | 105.6 |
assignment consistent with the 2D NMR spectrum of RO-K5 (RO-derivative of N-acetylheparosan), spectrum not shown
assignment consistent with the 2D NMR spectrum of RO-derivative of N-acetylated bovine lung heparin
published in [14]
R – remnant generated by hydrolysis of glycol-split uronic acids; data obtained from 2D NMR spectrum of the fraction of heparinase-digested RO-enoxaparin, containing ΔU2S-ANS6S and ΔU2S-ANS6S-R
reported in [13] for RO-heparins
present work
from NMR analysis of RO-dalteparin (this cross peak correlates with CH2OH in the TOCSY spectrum indicating that it is a glycol-split uronic acid); A* = ANS3S(6S)
