Fig. 4.
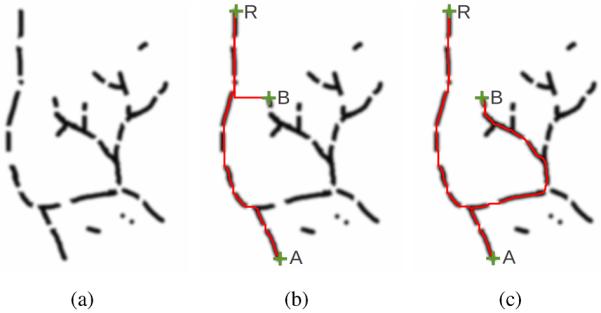
Path extraction on a 2D phantom data set of a tree-like structure. (a) Cost image of the phantom data set with some disturbances in the image (areas of high costs on the path); areas of low cost are dark. (b) Paths extracted between the root of the tree structure (R) and selected endpoints (A and B) using a conventional minimum cost path extraction algorithm. For point B, the algorithm shortcuts through an area with high costs instead of extracting a longer path with smaller disturbances on the path. (c) Result of the proposed algorithm. The algorithm robustly handles the disturbances on the paths and avoids shortcuts.
