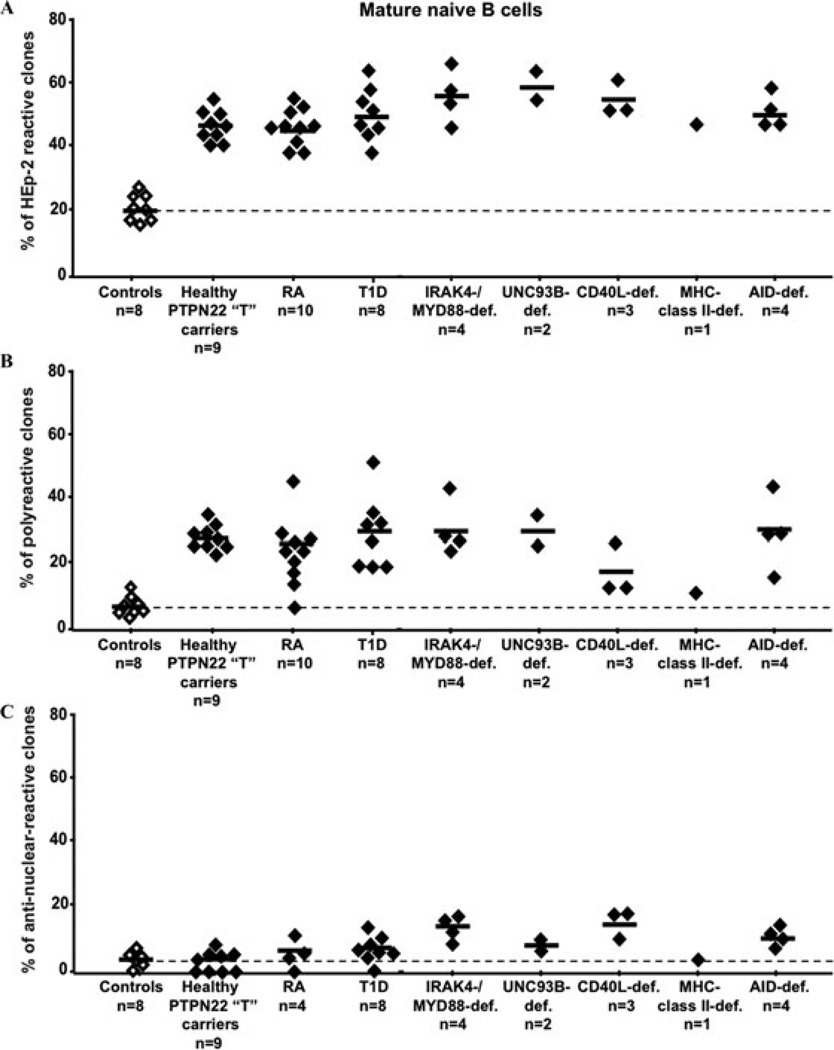
Figure 3.
Specific defective peripheral B cell tolerance checkpoint in CD40L- and MHC class II-deficient patients. The frequencies of HEp-2 reactive (A), polyreactive (B), and antinuclear (C) mature naive B cells are compared between controls (open diamonds), subjects with the PTPN22 “T” risk allele, patients with diverse PID, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and type 1 diabetes (T1D) (black diamonds). Defects in CD40L expression or antigen presentation through MHC class II molecules specifically either interfere with the removal or fail to prevent the accumulation of autoreactive B cells in the periphery. All other subjects who presented central B cell tolerance defects also display large numbers of autoreactive B cells in their mature naive B cell compartment.