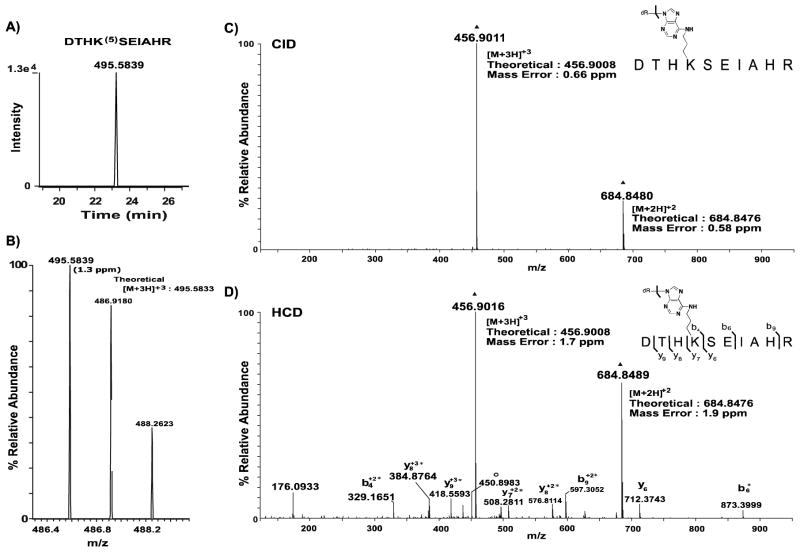
Figure 5. Extracted ion chromatograms and corresponding MS spectra of precursor ions observed for OPdA-modified peptide DTHK(5)SEIAHR.
A, The XIC was generated as described in Figure 4A. B, The mass spectrum for the precursor peptide is annotated with the observed m/z values provided above the corresponding monoisotopic peak. The theoretical value of the precursor ion is adjacent to the observed peak and was used to calculate ppm mass error (shown in parentheses) for the identified peptide form. C, High-resolution targeted CID spectrum of precursor 5-adducted DTHK(5)SEIAHR peptide (m/z: 495.58). Dissociation of the glycosidic bond, as indicated by the bracket, results in the formation of intact peptide products with mass shifts consistent with 6- adduction. This peptide is present as both doubly- and triply-protonated ions, denoted by ▲. D, High-resolution targeted HCD spectrum of precursor 5-adducted DTHK(5)SEIAHR peptide (m/z: 495.58). Glycosidic bond cleavage was observed in addition to peptide backbone fragmentation. Asterisks indicate residues with mass shifts consistent with adduction by 6. Water loss from the 6-adducted DTHK(6)SEIAHR product is denoted with ○, and the intact 6-adducted DTHK(6)SEIAHR peptide product is denoted with ▲. Mass errors observed for the [M+2H]+2 and [M+3H]+3 6-adducted peptide products are provided in both spectra and mass errors for all product ions observed were less than 4.5 ppm. Unless otherwise indicated, product ions are singly-protonated.