Figure 1.
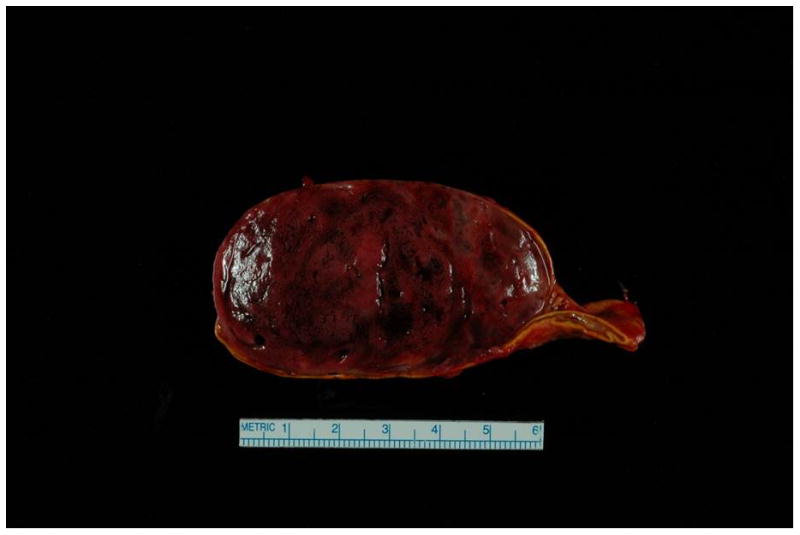
Surgical specimen of the adrenal pheochromocytoma.
Case presentation - Patient was a 31 year old P6G5 with a history of chronic hypertension requiring medications intermittently in the past, and a history of preeclampsia with her first pregnancy, with subsequent unremarkable pregnancies. She was admitted at 34 weeks due to systolic BP > 200 mm Hg, as well as 3+ protein on dipstick, elevated AST (57 U/L), serum creatinine of 1.2 mg/dL and uric acid of 10.1 mg/dL. The constellation of clinical findings and laboratory abnormalities was considered to be consistent with preeclampsia. She received IV magnesium sulfate and labetalol, and underwent C-section at 34 and 4/7 weeks, and gave birth to a healthy male infant. Systolic BPs remained in the 180s mm Hg post-delivery, and she was transferred to the ICU for hypertensive urgency. Work-up for secondary causes revealed a 3.2 × 6.2 × 5.3 cm heterogenous lesion in the right adrenal gland, and MRI was consistent with pheochromocytoma. The level of plasma free normetanephrine was 26.2 nmol/L (normal < 0.90 nmol/L), and the 24-hour urine showed significantly elevated levels of norepinephrine and normetanephrine. She received phenoxybenzamine, nicardipine and propranolol. She underwent a right total adrenalectomy (photograph of mass shown) and was able to be tapered off her BP medications.
