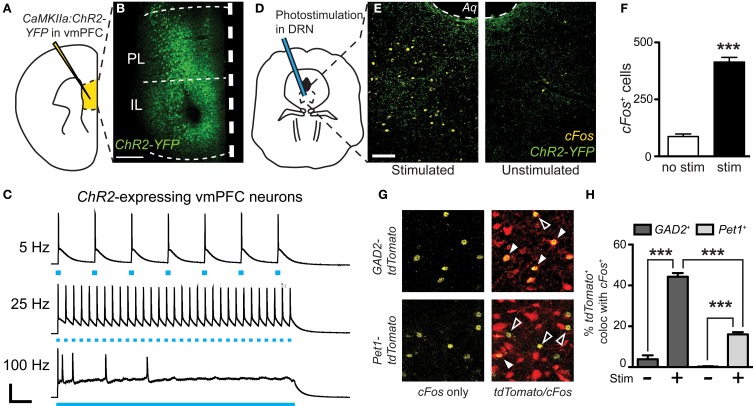
Figure 4.
Preferential cFos induction in GABA neurons after photostimulation of vmPFC terminals in the DRN. (A) CaMKIIa-driven ChR2-YFP was injected in the vmPFC of GAD2-tdTomato or Pet1-tdTomato mice. (B) After allowing 6 weeks, robust expression of ChR2-YFP was achieved. Scale bar 25 μm. (C) Fluorescent neurons in layer V of the vmPFC were recorded. Current-clamp traces of YFP+ vmPFC neurons demonstrate temporal fidelity of ChR2-mediated photocurrents at 5 and 25 Hz, and loss of precision at 100 Hz. Scale bar 40 pA, 0.2 s. (D) At the same time point post-injection (6 weeks), vmPFC terminals in the DRN were photostimulated for 20 min using 473 nm light (10 mW, 25 Hz, 10 ms pulse width). (E) cFos immunofluorescence was evaluated after photostimulation to indicate neuronal activation. Scale bar 50 μm. (F) Photostimulation resulted in a significant increase in total cFos expression with no difference between genotype (Student's t-test, ***p < 0.001). (G) Quantification of cFos colocalization with native tdTomato fluorescence was used to determine the neuronal populations activated. Closed arrows indicate colocalized neurons. (H) Without laser stimulation there is minimal cFos expression. After photoactivation of vmPFC terminals there were increases in neuronal activation of both GABA and 5-HT neurons, however a much higher percentage of GAD2-tdTomato neurons colocalize with cFos (Two-Way ANOVA, Fisher post-hoc, ***p < 0.001).