Figure 1.
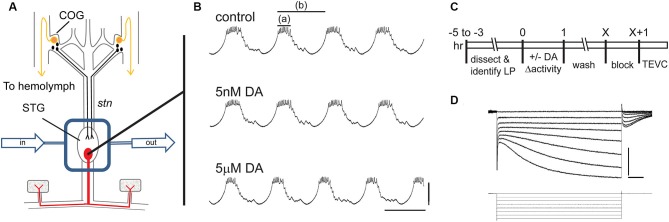
The experimental model. (A) The stomatogastric nervous system is dissected and pinned in a dish. Dopamine neurons (black) in the commissural ganglia (COGs) project through the stomatogastric nerve (stn) to the STG. The L-cells (gold) in the COGs are the source of neurohormonal DA that constantly bathes the STG. In these experiments, the STG is isolated with a Vaseline well (rectangle) and constantly superfused throughout the experiment (arrows). There are ~30 neurons in the STG including the single LP neuron that is illustrated in red. (B) Intracellular LP recordings from a typical experiment where the STG was sequentially superfused with saline (control), 5 nM DA and 5 µM DA. Note that 5 µM but not 5 nM produced a significant decrease in LP burst duration (a) and cycle period (b). Scale bars are 20 mV and 500 ms. (C) Diagram of typical somatic TEVC experiments to measure persistent changes in LP Ih. (D) Representative LP Ih recording elicited with a series of hyperpolarizations from −50 mV to −120 mV in 10 mV increments from a holding potential of −50 mV; current (top) and voltage (bottom) traces are shown; scale bars are 5 nA and 500 ms.
