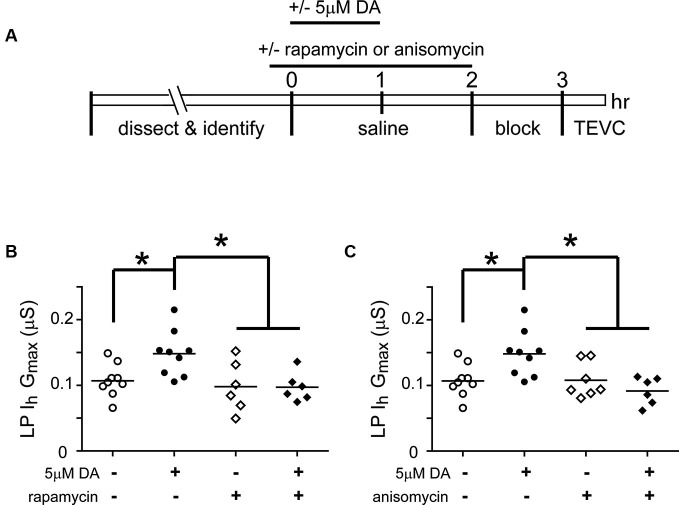
Figure 4.
The DA- and activity-dependent persistent increase in LP IhGmax is mediated by an mTOR-dependent translational mechanism. (A) Diagram of the experimental protocol. (B) The mTORC1 inhibitor, rapamycin (100 nM), prevented the increase in LP Ih Gmax normally elicited by 5 µM DA but had no effect on its own. LP Ih Gmax is plotted for each treatment group; each symbol represents one experiment; the horizontal bars represent the means. Asterisks indicate significant differences as determined using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc tests that made all pairwise comparisons, F(3,26) = 5.015, p = 0.0071. (C) The translation inhibitor, anisomycin (30 µM), had no effect on its own but prevented the persistent increase in LP Ih Gmax elicited by 5 µM DA. Asterisks indicate significant differences as determined using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc tests, F(3,27) = 5.976, p = 0.0029.