Fig. 2.
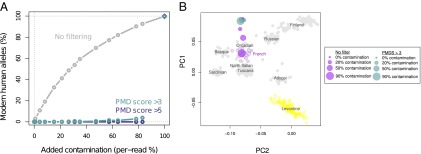
Artificial mtDNA and autosomal contamination experiments. (A) Artificial contamination represented by sequences from a present day human (French) was added to a sequence dataset from a Croatian Neandertal (Vindija 33.16). Final per base pair contamination was estimated using diagnostic mtDNA positions that differentiate Neandertals from modern humans. Up to 90% per base pair contamination levels can be reduced to negligible levels using the PMDS approach. (B) Artificial contamination represented by sequences from a present day human (French) was added to a sequence dataset from Neolithic Scandinavian hunter-gatherers. SNPs were extracted with and without filtering for PMDS, and a principal component analysis together with European and Levantine populations was performed for the different levels of contamination. The PCs were Procrustes transformed for each separate analysis (8).
