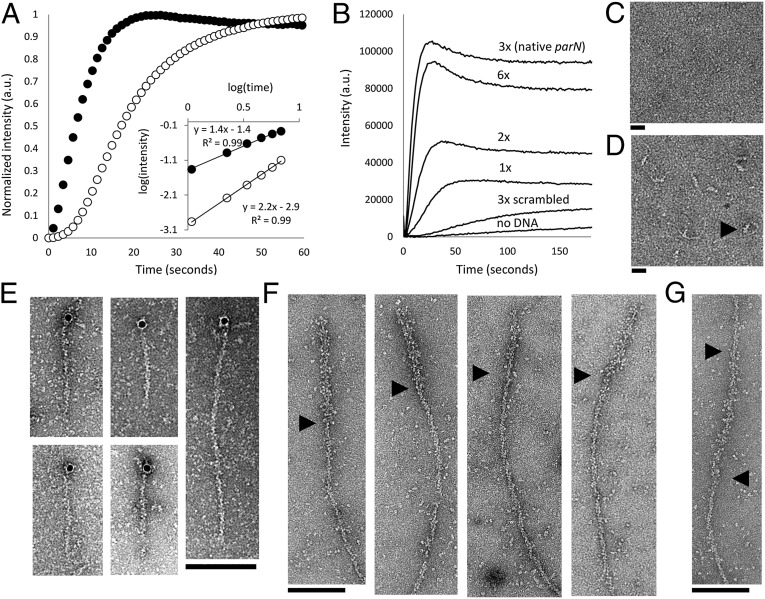
Fig. 3.
AlfB forms a complex on parN DNA that nucleates AlfA polymerization and binds to the ends of polar filaments. (A) Intensity-normalized light scattering of 300 nM of AlfA polymer formed in the absence (○) and presence (●) of 1.3 µM AlfB and 50 nM parN. The nucleation-dominated lag phase of polymerization is dramatically reduced with AlfB and parN, and the change in the slope of early time points on a log-log plot indicates that the number of steps of polymer assembly is reduced (5 mM ATP). Buffer, 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 100 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM DTT. (B) Stabilization of AlfA by the parN/AlfB complex depends on the valency of AlfB-binding DNA repeats. Each reaction contains 2.1 µM AlfA, 1.3 µM AlfB, and 75 nM individual repeats. For example, the sequence containing a single repeat is present at 75 nM, whereas the native parN sequence, with three repeats, is present at 25 nM (2 mM ATP). Buffer as above. (C) 500 nM AlfB does not form a complex in the presence of 50 nM parC (the centromere of the ParM system). Buffer, 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 30 mM KCl, 10 mM (NH4)2SO4, 1 mM DTT, and 1 mM EDTA. (Scale bar, 20 nM.) (D) A complex is formed in the presence of parN. (Scale bar, 20 nM.) Black arrowhead points to a representative complex. Buffer as above. (E) AlfB-parN binds to the ends of filaments; 10-nm colloidal gold particles coated in streptavidin localize predominantly to the ends of 3.5 µM AlfA KK21AA KK101AA filaments in the presence of 1.3 µM AlfB and 120 nM parN-biotin (2 mM ATP). Buffer, 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 100 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM DTT. (F) Filaments are polar. KK21AA KK101AA filaments (3 μM total monomer concentration) was polymerized off of AMP-PNP stabilized seeds composed of 50% KK21AA KK101AA AlfA and 50% AlfA-biotin decorated with an excess of streptavidin and diluted to 100 nM. Black arrowheads show boundaries between streptavidin-decorated seeds and normal filaments. Buffer as above. (G) A subset (21%) of these labeled filaments displays the seed in the middle. This configuration may be due to bundling of the WT polymer or streptavidin cross-linking within the seed. Buffer as above. Black arrowheads denote ends of the streptavidin seed.