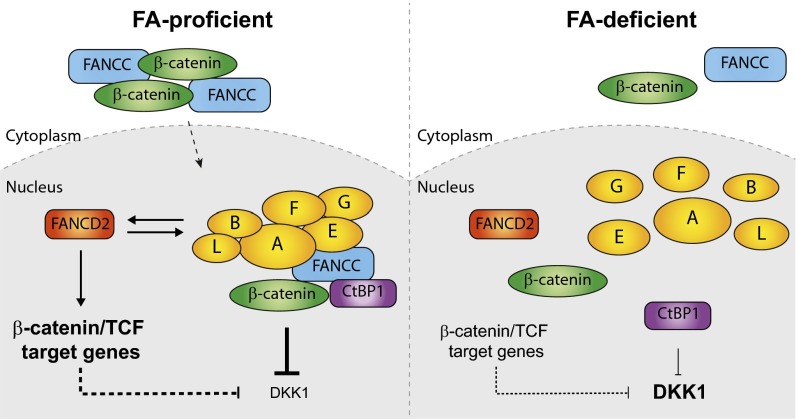
Fig. 7.
Proposed model of a dual mechanism by which the FA pathway regulates expression of DKK1. (Left) In the presence of an intact FA pathway (FA-proficient), FANCC and β-catenin efficiently accumulate and localize into the nucleus after GSK3β inhibition. In the nucleus, FANCC forms a complex with CtBP1 and β-catenin and represses DKK1. The FA core complex via FANCD2 enhances expression of other β-catenin/TCF target genes. FANCD2 influences the stability or expression of FA core complex proteins and, subsequently, DKK1 expression. (Right) In the absence of a functional FA pathway (FA-deficient), FANCC and β-catenin do not efficiently accumulate into the nucleus. As a result, FANCC fails to efficiently repress DKK1. Lack of FA core complex activity results in reduced expression of β-catenin/TCF targets and increased DKK1 expression.