Fig. 1.
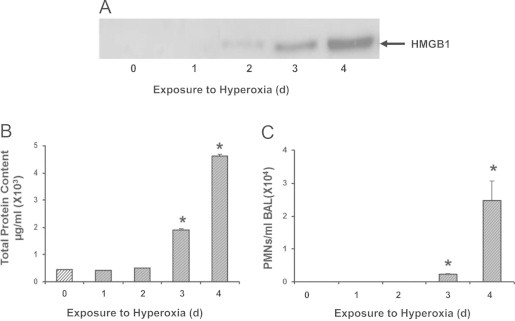
Hyperoxia-induced lung injury is associated with increased accumulation of HMGB1 in the airways. C57BL/6 mice were exposed to ≥99% O2 for indicated days (d) or remained at RA (Exposure to hyperoxia = 0 d). Levels of airway HMGB1 were analyzed by western blot analysis in mouse bronchoalveolar lavage fluids (BALF). Blots shown are representative of three independent experiments with similar results (A). Total protein content (B) and neutrophil (PMNs) infiltration (C) in the airway were analyzed as markers of inflammatory ALI. Data represent means±SE from two independent experiments, n=9 mice per group. ⁎, Statistically significant vs. the values of the control group that remained at RA (Exposure to hyperoxia = 0 d), P<0.05.
