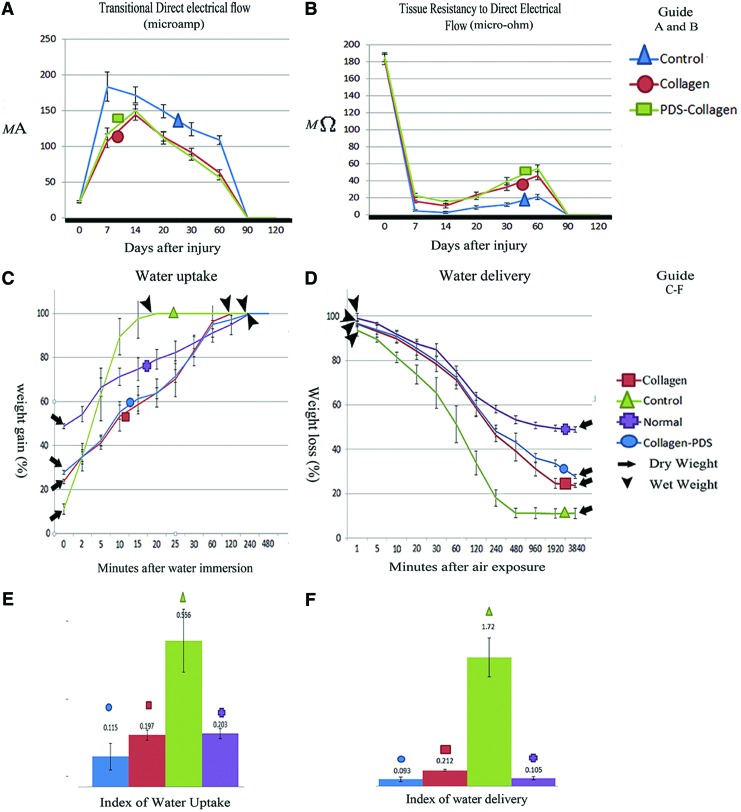
FIG. 4.
Bioelectrical and biophysical characteristics of the injured tendons. The treated tendons with collagen and collagen-PDS prostheses had a significantly lower transitional direct electrical flow (A) (p<0.05) and higher tissue resistancy to direct electrical flow (B) (p<0.05) compared to the ICTs. However there were no significant differences between the treated groups (p>0.05). The injured tendons treated with collagen and collagen-PDS prosthesis had a more similar diagrammatic pattern of water uptake (C) and water delivery (D) to the normal pattern at various time points, compared to the ICTs, so that, in the treated tendons the indices of water uptake (E) and delivery (F) were significantly lower than the ICTs and was close to normal value. Compared to the injured collagen tendons, the Collagen-PDS tendons showed significantly the lower indices of water uptake and water delivery (p<0.05). Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea